Difference between revisions of "Sound"
(→Pitch) |
(→Key Stage 3) |
||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
|[[File:VibrateSound1.gif|center]] | |[[File:VibrateSound1.gif|center]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
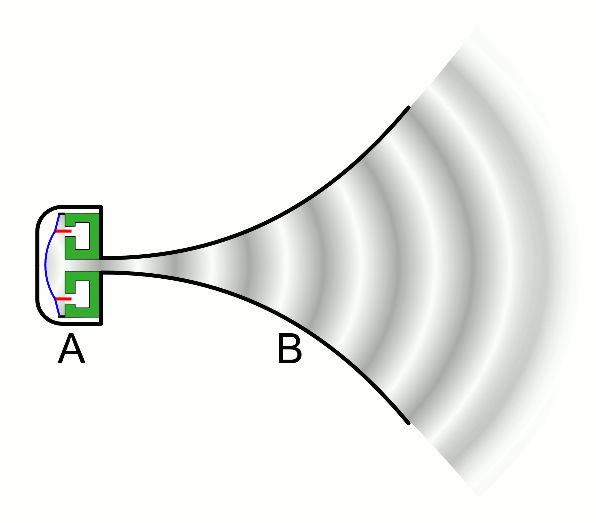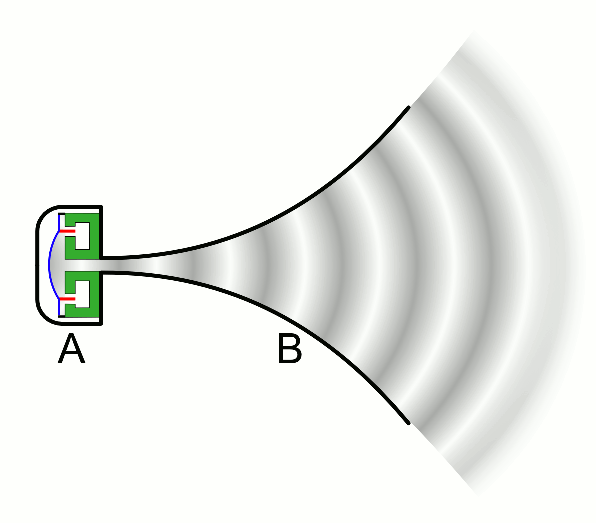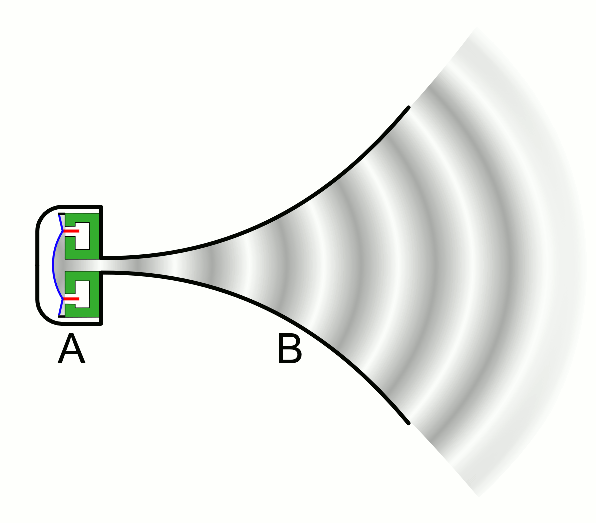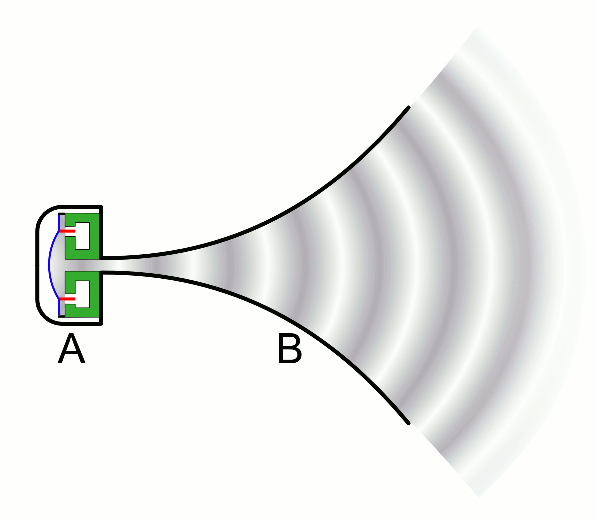
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This animation shows a [[speaker]] creating a sound by making a [[wave]] of compression (dark grey) that passes through the [[air]]. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This animation shows a [[speaker]] creating a [[sound]] by making a [[wave]] of compression (dark grey) that passes through the [[air]]. |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 142: | Line 142: | ||
|[[File:OscilloscopeScreen6.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:OscilloscopeScreen6.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
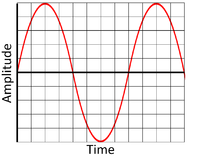
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This is a high amplitude wave showing a [[sound]] with a high volume, so it is loud. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This is a high [[amplitude]] wave showing a [[sound]] with a high [[Volume (Sound)|volume]], so it is loud. |
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | ||
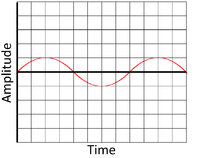
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This is a low amplitude wave showing a [[sound]] with a low volume so it is quiet. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This is a low [[amplitude]] wave showing a [[sound]] with a low [[Volume (Sound)|volume]] so it is quiet. |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 158: | Line 158: | ||
|[[File:OscilloscopeScreen3.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:OscilloscopeScreen3.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
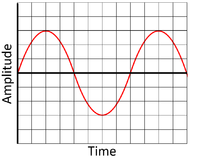
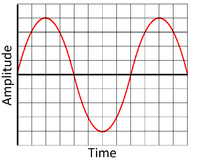
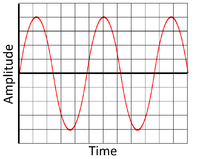
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This is a low frequency wave showing a [[sound]] with a low pitch, so it is a deep sound. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This is a low [[frequency]] wave showing a [[sound]] with a low pitch, so it is a deep [[sound]]. |
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" | | ||
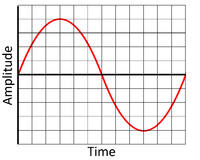
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This is a high frequency wave showing a [[sound]] with a high pitch. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This is a high [[frequency]] [[wave]] showing a [[sound]] with a high [[pitch]]. |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 16:36, 18 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 1
We hear sound with our ears.
Meaning
Sound is something that we hear with our ears.
About Sound
- A sound can be loud or quiet.
- A sound can be low or high pitched.
Examples
| The sound of a mouse's squeak is very 'high pitched'. | A tuba makes a deep or 'low pitched' sound. |
| Shouting, screaming and yelling are all loud sounds. | Whispering is a very quiet sound. |
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Sound is a vibration that passes through the air to our ears.
About Sound
- Sounds are caused by materials vibrating.
- Sound has to travel through a medium. If there is no medium, sound cannot get form one place to another.
- Sound travels through the air because it makes the air vibrate. If there were no air sound could not travel to our ears.
- Sounds can be high or low pitched.
- Sounds can be loud or quiet.
Pitch
Size
| A small 'soprano' saxophone makes a high pitched sound. | An 'alto' saxophone makes the second highest pitch. | A tenor saxophone makes the second lowest pitch. | A large 'bass' saxophone makes a low pitched sound. |
Thickness of Strings
| A regular guitar has thin strings and can make high pitched sounds. | A 'bass' guitar has thick strings and makes low pitched sounds. |
Length of Strings
| The shorter strings on a harp make a higher pitched sound. |
Tightness of Strings
| The pegs on the end of a stringed instrument can make the strings tighter or looser. |
Volume
| When you hit a drum hard, it makes a louder sound because the vibration is bigger. | When you pluck a guitar string harder, it makes a louder sound because the vibration is bigger. | Blow harder down a tube it makes a louder sound because the vibration is bigger. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Sound is a pressure wave that transfers energy and information through a medium.
About Sound
- Sound is a longitudinal wave.
- Sound is caused by objects vibrating. The vibration is then passed through a medium as a wave of compression.
- Sound is transmitted by particles colliding with one another.
- The speed of sound through air is 340m/s.
| This is animation shows how sound travels along a material by particles colliding with one another. |
| Sound Waves |
| This animation shows a speaker creating a sound by making a wave of compression (dark grey) that passes through the air. |
Medium
- Sound waves can pass through solids, liquids and gases but sound cannot pass through a vacuum.
- Sound travels fastest through a solid because the particles are already touching so they have little distance to travel to pass on the vibration.
- Sound travels the slowest through a gas because the particles in a gas are spread far apart so they take some time before they collide with the next particle to pass on the vibration.
| A diagram showing the particle model for solids, liquids and gases. |
Sound Volume
- The volume of a sound is how loud or quiet it is.
- Volume is determined by the amplitude of the wave (how much the wave vibrates).
| This is a high amplitude wave showing a sound with a high volume, so it is loud. | This is a low amplitude wave showing a sound with a low volume so it is quiet. |
Pitch
- A sound can be a high pitch or low pitch.
- Pitch is determined by the frequency of the wave (how quickly the wave vibrates).
- The frequency of a sound wave is measures in Hertz (Hz).
| This is a low frequency wave showing a sound with a low pitch, so it is a deep sound. | This is a high frequency wave showing a sound with a high pitch. |