Difference between revisions of "Group 7"
(→Chemical Properties) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
: '''Halogens''' all [[Chemical Reaction|react]] strongly as [[Bleaching Agent|bleaching agents]]. | : '''Halogens''' all [[Chemical Reaction|react]] strongly as [[Bleaching Agent|bleaching agents]]. | ||
: '''Halogens''' all produce [[acid]]s when combined with [[Hydrogen]]. | : '''Halogens''' all produce [[acid]]s when combined with [[Hydrogen]]. | ||
| − | : '''Halogens''' are [[ | + | : '''Halogens''' are [[toxic]] to [[bacteria]] and are used in [[disinfectant]]s. |
===Physical Properties=== | ===Physical Properties=== | ||
Revision as of 15:38, 26 November 2018
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
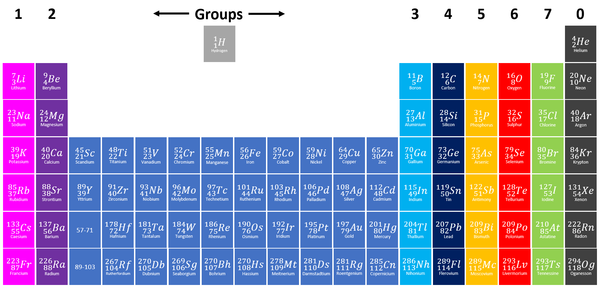
Group 7 elements, also known as Halogens on the Periodic Table are the elements which have 7 electrons in their outer shell.
| Group 7 elements are shown in green at the right of the Periodic Table. |
About the Halogens
- The Halogens have similar chemical properties because they all have 7 electrons on their outer shell.
- Halogens all produce ions with a -1 relative charge because they gain an electron in chemical reactions.
The Halogens in order from most reactive to least reactive are:
Chemical Properties
- The reactivity of Halogens decreases as you go down the Periodic Table.
- Halogens all react strongly as bleaching agents.
- Halogens all produce acids when combined with Hydrogen.
- Halogens are toxic to bacteria and are used in disinfectants.
Physical Properties
The physical properties of Halogens changes significantly as you go down the Periodic Table:
- Fluorine - A yellow gas at room temperature.
- Chlorine - A green gas at room temperature.
- Bromine - A brown liquid at room temperature.
- Iodine - A purple solid at room temperature.
- Astatine -A dark purple solid at room temperature.
- The density, melting point and boiling point all increase as you go down the Periodic Table.