Difference between revisions of "Diffusion"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
: [[Diffusion]] cannot happen in a [[solid]] because the [[particle]]s are held in fixed positions. | : [[Diffusion]] cannot happen in a [[solid]] because the [[particle]]s are held in fixed positions. | ||
: In [[diffusion]] the particles always spread from a high [[concentration]] where there is lots of the substance, to a low [[concentration]] where there is less of the substance. | : In [[diffusion]] the particles always spread from a high [[concentration]] where there is lots of the substance, to a low [[concentration]] where there is less of the substance. | ||
| − | : [[Diffusion]] stops when all | + | : [[Diffusion]] stops when all [[substance]]s are spread out equally and there is no longer a [[Concentration Gradient|concentration gradient]]. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 10:25, 27 September 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
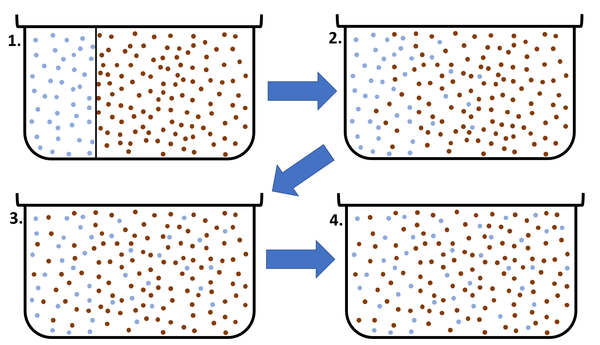
Diffusion is when particles spread from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
About Diffusion
- Diffusion can only happen in a fluid which means a liquid or a gas because the particles can move past each other.
- Diffusion cannot happen in a solid because the particles are held in fixed positions.
- In diffusion the particles always spread from a high concentration where there is lots of the substance, to a low concentration where there is less of the substance.
- Diffusion stops when all substances are spread out equally and there is no longer a concentration gradient.
| This diagram shows a high concentration of blue particles on the left separated from the red particles by a barrier. When the barrier is removed the blue particles diffuse to the area of lower concentration on the right. Diffusion continues until all particles are equally spread. |