Difference between revisions of "Condensing"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 2== | ==Key Stage 2== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Condensing''' is when a [[gas]] turns into a [[liquid]]. |
| + | : [[Noun]]: '''Condensation''' | ||
: [[Verb]]: '''To condense''' | : [[Verb]]: '''To condense''' | ||
| + | : [[Present Participle]]: '''Condensing''' | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 13: | Line 15: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ===About | + | ===About Condensing=== |
: Cooling a [[gas]] will cause it to '''condense''' into a [[liquid]]. | : Cooling a [[gas]] will cause it to '''condense''' into a [[liquid]]. | ||
: '''Condensing''' is a [[Reversible Changes|reversible]] process. When a [[gas]] '''condenses''' into a [[liquid]] you can [[Evaporating|evaporate]] that [[liquid]] back into a [[gas]]. | : '''Condensing''' is a [[Reversible Changes|reversible]] process. When a [[gas]] '''condenses''' into a [[liquid]] you can [[Evaporating|evaporate]] that [[liquid]] back into a [[gas]]. | ||
| − | : You may have seen water condensing. | + | : You may have seen water '''condensing'''. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |[[Water Vapour]] in the [[air]] '''condenses''' into [[liquid]] [[water]] onto a cold bottle. | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |[[Water Vapour]] in the [[air]] '''condenses''' into [[liquid]] [[water]] onto a cold bottle. | ||
| style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The [[Steam]] coming out of kettle '''condenses''' into a cloud of [[liquid]] [[water]] droplets. | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The [[Steam]] coming out of kettle '''condenses''' into a cloud of [[liquid]] [[water]] droplets. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | '''Freezing''' is when a [[liquid]] turns into a [[solid]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Condensing=== | ||
| + | : '''Condensing''' is a [[Reversible Changes|reversible]] process. When a [[gas]] '''condenses''' into a [[liquid]] you can [[Evaporating|evaporate]] that [[liquid]] back into a [[gas]]. | ||
| + | : Cooling a [[gas]] will cause it to '''condense''' into a [[liquid]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ When you cool a [[gas]]: | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ParticleModelCondensing.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
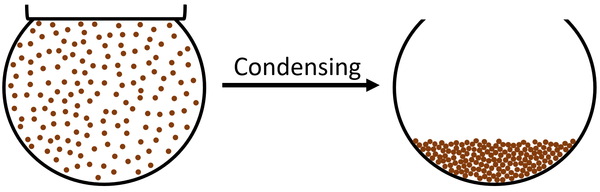
| + | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:left;" |The [[particle]]s in the [[gas]] slow down until they are slow enough that [[force]]s between the [[particle]]s start to hold them together. The [[particle]]s end up touching but can still move past each other which makes the [[State of Matter|state]] a [[liquid]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 15:55, 22 September 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Condensing is when a gas turns into a liquid.
- Noun: Condensation
- Verb: To condense
- Present Participle: Condensing
| A gas will condense to become a liquid. |
About Condensing
- Cooling a gas will cause it to condense into a liquid.
- Condensing is a reversible process. When a gas condenses into a liquid you can evaporate that liquid back into a gas.
- You may have seen water condensing.
| Water Vapour in the air condenses into liquid water onto a cold bottle. | The Steam coming out of kettle condenses into a cloud of liquid water droplets. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Freezing is when a liquid turns into a solid.
About Condensing
- Condensing is a reversible process. When a gas condenses into a liquid you can evaporate that liquid back into a gas.
- Cooling a gas will cause it to condense into a liquid.
| The particles in the gas slow down until they are slow enough that forces between the particles start to hold them together. The particles end up touching but can still move past each other which makes the state a liquid. |