Difference between revisions of "Solid"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[File:ParticleModelSolid.png|right|300px|thumb|The [[Particle Model]] of a [[solid]].]] | ||
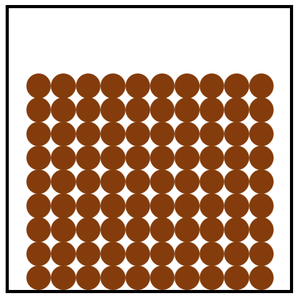
A [[State of Matter|state of matter]] where all the [[Particle|particles]] are touching and in a regular arrangement. | A [[State of Matter|state of matter]] where all the [[Particle|particles]] are touching and in a regular arrangement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Solids=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
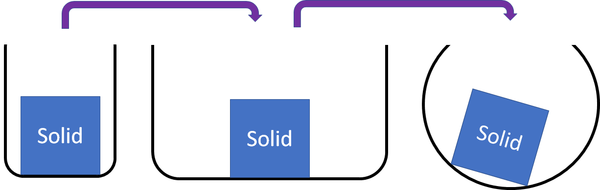
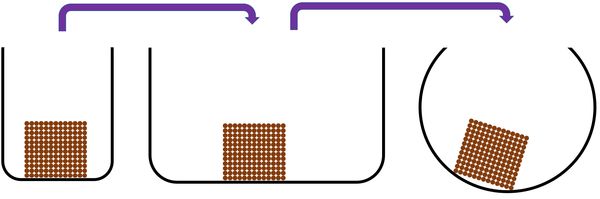
| + | |+ Solids are a '''state of matter''' that: | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ParticleModelSolidPour.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | *A [[solid]] cannot be poured because the [[particle]]s are in fixed positions. | ||
| + | *[[Solid]]s hold their shape if you leave them alone because the [[particle]]s are in fixed positions. | ||
| + | *[[Solid]]s do not flow because the [[particle]]s are in fixed positions. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
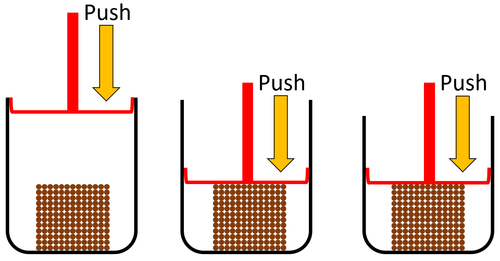
| + | |[[File:ParticleModelSolidSquash.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
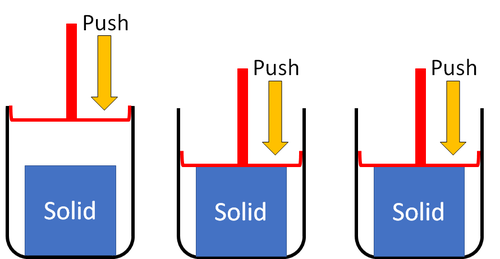
| + | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:left;" |'''Solids''' cannot be squashed into a smaller size because the [[particle]]s are already touching so they can't get any closer together. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 11:16, 22 September 2018
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Solid is a state of matter that holds its shape and cannot be squashed into a smaller space.
About Solids
- Solids can be described with texture.
|
| Solids cannot be squashed into a smaller size. You can change their shape by squashing, but their size stays the same. |
Examples of solid materials:
- Brick
- Wood
- Plastic
- Glass
- Ice
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A state of matter where all the particles are touching and in a regular arrangement.
About Solids
| Solids cannot be squashed into a smaller size because the particles are already touching so they can't get any closer together. |