Difference between revisions of "Electron"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
===About Electrons=== | ===About Electrons=== | ||
: [[Electron]]s have a [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of -1 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass|relative atomic mass]] of 1/1860. | : [[Electron]]s have a [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of -1 and a [[Relative Atomic Mass|relative atomic mass]] of 1/1860. | ||
| + | : The [[electron]]s and their [[Electron Orbital|shells]] are responsible for the chemistry of an [[atom]]. | ||
| + | : When [[atom]]s [[bond]] to form [[molecule]]s some [[atom]]s can share their [[electron]]s forming a [[Covalent Bond]], some transfer an [[electron]] from one [[atom]] to another forming an [[Ionic Bond]] while others allow [[electron]]s to pass freely between many [[atom]]s forming a [[Metallic Bond]]. | ||
Revision as of 14:16, 24 November 2018
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
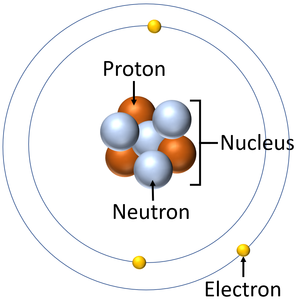
An electron is a small particle found orbiting the centre of an atom.
About Electrons
- Electrons negatively charged.
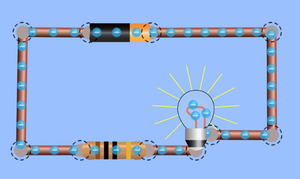
- In conductors electrons can pass easily from one atom to the next.
- When electrons move it is called an electrical current.
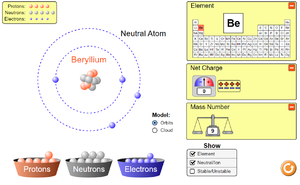
To see how electrons are arranged around the nucleus of atoms or to see how electrons move around a circuit click on the pictures below to play a PHET simulation.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Electron is a negatively charged particle found orbit the nucleus of an atom in electron shells.
About Electrons
- Electrons have a relative atomic charge of -1 and a relative atomic mass of 1/1860.
- The electrons and their shells are responsible for the chemistry of an atom.
- When atoms bond to form molecules some atoms can share their electrons forming a Covalent Bond, some transfer an electron from one atom to another forming an Ionic Bond while others allow electrons to pass freely between many atoms forming a Metallic Bond.