Difference between revisions of "Melting"
(→Meaning) |
(→Key Stage 3) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | '''Melting''' is an [[endothermic]] process | + | '''Melting''' is an [[endothermic]] process in which a [[solid]] turns into a [[liquid]]. |
===About Melting=== | ===About Melting=== | ||
Revision as of 18:01, 29 September 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
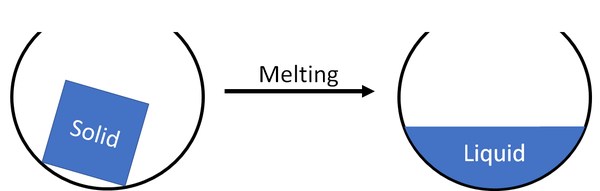
Melting is when a solid turns into a liquid.
- Verb: To melt
- Present Participle: Melting
| A solid will melt and become a liquid. |
About Melting
- Most solids can be melted to become a liquid.
- Melting is a reversible process. When a solid melts you can always freeze it back into a solid.
- You may have seen these solids melt
- Ice
- Wax
- Chocolate
- Butter
Examples
| Some ice cubes melt to make water. | Wax melts because of the flame. |
| Chocolate can melt in your mouth because your mouth is warm. | You can melt butter in a frying pan. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
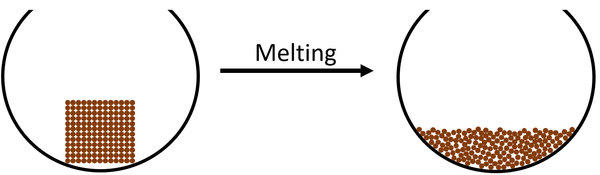
Melting is an endothermic process in which a solid turns into a liquid.
About Melting
- Most solids can be melted to become a liquid.
- Melting is a reversible process. When a solid melts you can always freeze it back into a solid.
- A solid can be melted by heating it.
| The particles in the solid vibrate faster until they vibrate fast enough that they break the bonds holding them in fixed positions. The particles become able to move past each other but are still touching which makes the state a liquid. |