Difference between revisions of "Electromagnetic Interaction"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 5== ===Meaning=== The '''electromagnetic interaction''' is the mechanism by which all particles with charge affect one another. ===About...") |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|[[File:ElectromagneticForceGraph.png|center|400px]] | |[[File:ElectromagneticForceGraph.png|center|400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
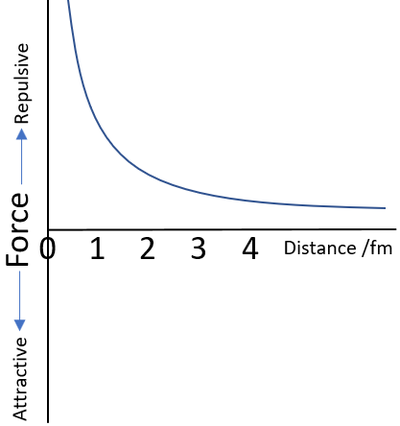
| − | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:center;" |This [[graph]] shows the strength of the [[force]] between two [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. The '''electromagnetic interaction''' between like [[Electrical Charge|charges]] is [[Repel|repulsive]] with a range of 0 to ∞. The strength of the [[force]] reduces [[proportional]] to 1/r<sup>2</sup>. | + | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:center;" |This [[graph]] shows the strength of the [[force]] between two [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. The '''electromagnetic interaction''' between like [[Electrical Charge|charges]] is [[Repel|repulsive]] with a range of 0 to ∞. The strength of the [[force]] reduces [[proportional]] to 1/r<sup>2</sup> where r is the distance between the centre of the [[Electrical Charge|charge]] distribution of each [[particle]]. |
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:34, 18 July 2019
Key Stage 5
Meaning
The electromagnetic interaction is the mechanism by which all particles with charge affect one another.
About The Electromagnetic Interaction
- The electromagnetic interaction is one of the 4 fundamental interactions governing how subatomic particles affect one another.
- The electromagnetic interaction causes positively charged particles to repel one another, negatively charged particles to repel one another and opposite charges to attract one another.
- The electromagnetic interaction acts to repel protons from one another in the atomic nucleus.
- The electromagnetic interaction is mediated by photons.
| This graph shows the strength of the force between two protons in the nucleus. The electromagnetic interaction between like charges is repulsive with a range of 0 to ∞. The strength of the force reduces proportional to 1/r2 where r is the distance between the centre of the charge distribution of each particle. |