Difference between revisions of "Exchange Surface"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== '''Exchange surfaces''' are membranes that allow diffusion of substances across the membrane from a region of high concentratio...") |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|[[File:CellDiffusion2.png|center|300px]] | |[[File:CellDiffusion2.png|center|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
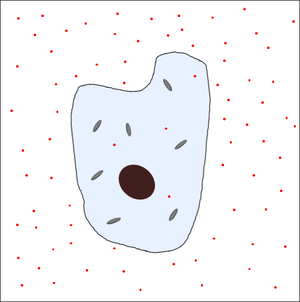
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |There is a high [[concentration]] of [[nutrient]]s outside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] so they diffuse through the [[Cell Membrane|membrane]] into the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |There is a high [[concentration]] of [[nutrient]]s outside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] so they [[Diffusion|diffuse]] through the [[Cell Membrane|membrane]] into the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. |
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[concentration]] of [[nutrient]]s inside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] and outside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] becomes the same. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[concentration]] of [[nutrient]]s inside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] and outside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] becomes the same. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|[[File:CellDiffusion4.png|center|300px]] | |[[File:CellDiffusion4.png|center|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
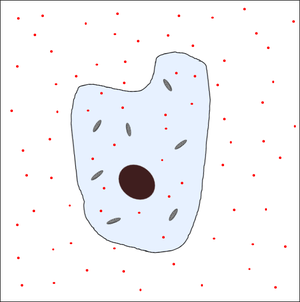
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |There is a high [[concentration]] of waste [[chemical]]s inside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] so they diffuse out through the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]]. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |There is a high [[concentration]] of waste [[chemical]]s inside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] so they [[Diffusion|diffuse]] out through the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]]. |
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[concentration]] of waste [[chemical]]s inside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] and outside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] becomes the same. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[concentration]] of waste [[chemical]]s inside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] and outside the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] becomes the same. | ||
|} | |} | ||
===About The Walls of the Alveoli as an Exchange Surface=== | ===About The Walls of the Alveoli as an Exchange Surface=== | ||
| − | : When [[air]] is [[inhale]]d into the [[lung]]s [[Oxygen]] [[diffuse]]s from the [[air]] across the walls of the [[alveoli]] and into the [[Red Blood Cell|red blood cells]]. | + | : When [[air]] is [[inhale]]d into the [[lung]]s [[Oxygen]] [[Diffusion|diffuse]]s from the [[air]] across the walls of the [[alveoli]] and into the [[Red Blood Cell|red blood cells]]. |
| − | : Before [[air]] is [[exhale]]d out of the [[lung]]s [[Carbon Dioxide]] [[diffuse]]s out of the [[blood]] through the walls of the [[alveoli]] and into [[air]] in the [[lung]]s. | + | : Before [[air]] is [[exhale]]d out of the [[lung]]s [[Carbon Dioxide]] [[Diffusion|diffuse]]s out of the [[blood]] through the walls of the [[alveoli]] and into [[air]] in the [[lung]]s. |
: The walls of the [[alveoli]] have several [[adaptation]]s to maximise the rate of [[diffusion]] across them: | : The walls of the [[alveoli]] have several [[adaptation]]s to maximise the rate of [[diffusion]] across them: | ||
:*The [[alveoli]] have thin walls to allow gas exchange to happen quickly. | :*The [[alveoli]] have thin walls to allow gas exchange to happen quickly. | ||
:*[[Alveoli]] are in groups to make a large [[Surface Area|surface area]] in the [[lung]] for gas exchange. | :*[[Alveoli]] are in groups to make a large [[Surface Area|surface area]] in the [[lung]] for gas exchange. | ||
:*The [[alveoli]] have a good [[blood]] supply to allow gas exchange with the [[blood]]. | :*The [[alveoli]] have a good [[blood]] supply to allow gas exchange with the [[blood]]. | ||
| − | :*The walls of the [[alveoli]] are kept moist to allow [[ | + | :*The walls of the [[alveoli]] are kept moist to allow [[gas]]es to [[dissolve]] into to the fluid for gas exchange with the [[blood]]. |
===About The Wall of the Small Intestines as an Exchange Surface=== | ===About The Wall of the Small Intestines as an Exchange Surface=== | ||
| − | : When food is consumed and [[ | + | : When food is consumed and [[Digestion|digested]] the [[nutrient]]s can [[Diffusion|diffuse]] across the walls of the [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] into the [[blood]] stream. |
: The wall of the [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] is [[adaptation|adapted]] to allow the movement of [[nutrient]]s from the food into the [[blood]] stream in the following ways: | : The wall of the [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] is [[adaptation|adapted]] to allow the movement of [[nutrient]]s from the food into the [[blood]] stream in the following ways: | ||
:*The [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] is long to give it a large [[Surface Area|surface area]]. | :*The [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] is long to give it a large [[Surface Area|surface area]]. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
===About Exchange Surfaces=== | ===About Exchange Surfaces=== | ||
| − | : [[Membrane]]s can be [[Partially Permeable Membrane|partially permeable]] so they only allow certain [[chemical]]s to | + | : [[Membrane]]s can be [[Partially Permeable Membrane|partially permeable]] so they only allow certain [[chemical]]s to [[Diffusion|diffuse]] through them. |
: [[Diffusion]] in [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] is a passive process which means it does not require [[energy]] to take place. | : [[Diffusion]] in [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] is a passive process which means it does not require [[energy]] to take place. | ||
: When [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] are surrounded by a high [[concentration]] of a [[nutrient]] then the [[nutrient]] will [[Diffusion|diffuse]] through the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] and into the [[Cell (Biology)|cells]]. | : When [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] are surrounded by a high [[concentration]] of a [[nutrient]] then the [[nutrient]] will [[Diffusion|diffuse]] through the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] and into the [[Cell (Biology)|cells]]. | ||
: When a [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] has filled with a large number of waste [[chemical]]s they will [[Diffusion|diffuse]] through the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] out of the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | : When a [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] has filled with a large number of waste [[chemical]]s they will [[Diffusion|diffuse]] through the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] out of the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | ||
| − | : [[Osmosis]] is when a [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] allows [[water]] to [[diffuse]] across the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] but not other [[ | + | : [[Osmosis]] is when a [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] allows [[water]] to [[Diffusion|diffuse]] across the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] but not other [[molecule]]s, particularly [[sugar]]s. |
: [[Active Transport]] takes place when an essential [[nutrient]] is needed in large quantities so [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] use [[energy]] to pump these [[nutrient]]s across the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] against the [[Concentration Gradient|concentration gradient]]. | : [[Active Transport]] takes place when an essential [[nutrient]] is needed in large quantities so [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] use [[energy]] to pump these [[nutrient]]s across the [[Cell Membrane|cell membrane]] against the [[Concentration Gradient|concentration gradient]]. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
*Thickness - The thinner the [[membrane]] the more quickly [[diffusion]] can take place across the [[membrane]]. | *Thickness - The thinner the [[membrane]] the more quickly [[diffusion]] can take place across the [[membrane]]. | ||
*[[Concentration Gradient]] - The greater the difference between the [[concentration]] on each side of the [[membrane]] the more quickly [[diffusion]] can take place across the [[membrane]]. | *[[Concentration Gradient]] - The greater the difference between the [[concentration]] on each side of the [[membrane]] the more quickly [[diffusion]] can take place across the [[membrane]]. | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Mitochondria]] - In cases of [[Active Transport|active transport]] [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] will have extra [[mitochondria]] to provide [[energy]] for this process. |
===About The Cell Membrane as an Exchange Surface=== | ===About The Cell Membrane as an Exchange Surface=== | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
===About The Walls of the Alveoli as an Exchange Surface=== | ===About The Walls of the Alveoli as an Exchange Surface=== | ||
| − | : When [[air]] is [[inhale]]d into the [[lung]]s [[Oxygen]] [[diffuse]]s from the [[air]] across the walls of the [[alveoli]] and into the [[Red Blood Cell|red blood cells]]. | + | : When [[air]] is [[inhale]]d into the [[lung]]s [[Oxygen]] [[Diffusion|diffuse]]s from the [[air]] across the walls of the [[alveoli]] and into the [[Red Blood Cell|red blood cells]]. |
| − | : Before [[air]] is [[exhale]]d out of the [[lung]]s [[Carbon Dioxide]] [[diffuse]]s out of the [[blood]] through the walls of the [[alveoli]] and into [[air]] in the [[lung]]s. | + | : Before [[air]] is [[exhale]]d out of the [[lung]]s [[Carbon Dioxide]] [[Diffusion|diffuse]]s out of the [[blood]] through the walls of the [[alveoli]] and into [[air]] in the [[lung]]s. |
: The walls of the [[alveoli]] have several [[adaptation]]s to maximise the rate of [[diffusion]] across them: | : The walls of the [[alveoli]] have several [[adaptation]]s to maximise the rate of [[diffusion]] across them: | ||
:*The [[alveoli]] have thin walls to allow gas exchange to happen quickly. | :*The [[alveoli]] have thin walls to allow gas exchange to happen quickly. | ||
:*[[Alveoli]] are in groups to make a large [[Surface Area|surface area]] in the [[lung]] for gas exchange. | :*[[Alveoli]] are in groups to make a large [[Surface Area|surface area]] in the [[lung]] for gas exchange. | ||
:*The [[alveoli]] have a good [[blood]] supply to allow gas exchange with the [[blood]]. | :*The [[alveoli]] have a good [[blood]] supply to allow gas exchange with the [[blood]]. | ||
| − | :*The walls of the [[alveoli]] are kept moist to allow [[ | + | :*The walls of the [[alveoli]] are kept moist to allow [[gas]]es to [[dissolve]] into to the fluid for gas exchange with the [[blood]]. |
===About The Wall of the Small Intestines as an Exchange Surface=== | ===About The Wall of the Small Intestines as an Exchange Surface=== | ||
| − | : When food is consumed and [[ | + | : When food is consumed and [[Digestion|digested]] the [[nutrient]]s can move across the walls of the [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] into the [[blood]] stream by [[diffusion]] or [[Active Transport|active transport]]. |
: The wall of the [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] is [[adaptation|adapted]] to allow the movement of [[nutrient]]s from the food into the [[blood]] stream in the following ways: | : The wall of the [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] is [[adaptation|adapted]] to allow the movement of [[nutrient]]s from the food into the [[blood]] stream in the following ways: | ||
:*The [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] is long to give it a large [[Surface Area|surface area]]. | :*The [[Small Intestine|small intestine]] is long to give it a large [[Surface Area|surface area]]. | ||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
:**The [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] in the walls of the [[villi]] have [[microvilli]] to provide an even bigger [[Surface Area|surface area]] for quicker [[diffusion]]. | :**The [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] in the walls of the [[villi]] have [[microvilli]] to provide an even bigger [[Surface Area|surface area]] for quicker [[diffusion]]. | ||
:***The [[microvilli]] have extra [[mitochondria]] to provide energy for [[Active Transport|active transport]]. | :***The [[microvilli]] have extra [[mitochondria]] to provide energy for [[Active Transport|active transport]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Exchange surfaces, pages 23-25, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''Exchange surfaces, pages 54-56, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Exchange surfaces, pages 60-62, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Exchange surfaces, page 60, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''Exchange surfaces, pages 257, 260, 261, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946748/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946748&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a4f0348fc37d0ba1bb52d27f8679581f ''Exchange surfaces, pages 87, 88, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Exchange surfaces, page 28, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945660/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945660&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=83aa4500ad7759e7f401a1c5ba5df758 ''Exchange surfaces, pages 34, 35, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359810/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359810&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=d768d99f1a06f7c12fab40e5aef85a55 ''Exchange surfaces, pages 72-73, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:41, 7 December 2019
Contents
- 1 Key Stage 3
- 2 Key Stage 4
- 2.1 Meaning
- 2.2 About Exchange Surfaces
- 2.3 Factors Affecting Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport across an Exchange Surface
- 2.4 About The Cell Membrane as an Exchange Surface
- 2.5 About The Walls of the Alveoli as an Exchange Surface
- 2.6 About The Wall of the Small Intestines as an Exchange Surface
- 2.7 References
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Exchange surfaces are membranes that allow diffusion of substances across the membrane from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
About Exchange Surfaces
- There are several exchange surfaces you should know:
- Cell Membranes
- The walls of alveoli
- The walls of the intestines.
About The Cell Membrane as an Exchange Surface
- When cells are surrounded by a high concentration of a nutrient then the nutrient will diffuse through the cell membrane and into the cells.
- When a cell has filled with a large number of waste chemicals they will diffuse through the cell membrane out of the cell.
| There is a high concentration of nutrients outside the cell so they diffuse through the membrane into the cell. | The concentration of nutrients inside the cell and outside the cell becomes the same. |
| There is a high concentration of waste chemicals inside the cell so they diffuse out through the cell membrane. | The concentration of waste chemicals inside the cell and outside the cell becomes the same. |
About The Walls of the Alveoli as an Exchange Surface
- When air is inhaled into the lungs Oxygen diffuses from the air across the walls of the alveoli and into the red blood cells.
- Before air is exhaled out of the lungs Carbon Dioxide diffuses out of the blood through the walls of the alveoli and into air in the lungs.
- The walls of the alveoli have several adaptations to maximise the rate of diffusion across them:
- The alveoli have thin walls to allow gas exchange to happen quickly.
- Alveoli are in groups to make a large surface area in the lung for gas exchange.
- The alveoli have a good blood supply to allow gas exchange with the blood.
- The walls of the alveoli are kept moist to allow gases to dissolve into to the fluid for gas exchange with the blood.
About The Wall of the Small Intestines as an Exchange Surface
- When food is consumed and digested the nutrients can diffuse across the walls of the small intestine into the blood stream.
- The wall of the small intestine is adapted to allow the movement of nutrients from the food into the blood stream in the following ways:
- The small intestine is long to give it a large surface area.
- The wall of the small intestine is thin to provide a short distance for nutrients to travel from food to the blood stream.
- The wall of the small intestine is covered in villi which are small folds, also increasing the surface area.
- Villi have capillaries inside them for a good blood supply to allow for quick diffusion into the blood.
- Villi have a large surface area to allow quicker diffusion.
- The cells in the walls of the villi have microvilli to provide an even bigger surface area for quicker diffusion.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Exchange surfaces are membranes that allow movement of substances by diffusion, osmosis or active transport.
About Exchange Surfaces
- Membranes can be partially permeable so they only allow certain chemicals to diffuse through them.
- Diffusion in cells is a passive process which means it does not require energy to take place.
- When cells are surrounded by a high concentration of a nutrient then the nutrient will diffuse through the cell membrane and into the cells.
- When a cell has filled with a large number of waste chemicals they will diffuse through the cell membrane out of the cell.
- Osmosis is when a cell membrane allows water to diffuse across the cell membrane but not other molecules, particularly sugars.
- Active Transport takes place when an essential nutrient is needed in large quantities so cells use energy to pump these nutrients across the cell membrane against the concentration gradient.
Factors Affecting Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport across an Exchange Surface
- Surface Area - The larger the surface area the more quickly diffusion can take place across the membrane.
- Thickness - The thinner the membrane the more quickly diffusion can take place across the membrane.
- Concentration Gradient - The greater the difference between the concentration on each side of the membrane the more quickly diffusion can take place across the membrane.
- Mitochondria - In cases of active transport cells will have extra mitochondria to provide energy for this process.
About The Cell Membrane as an Exchange Surface
- When cells are surrounded by a high concentration of a nutrient then the nutrient will diffuse through the cell membrane and into the cells.
- When a cell has filled with a high concentration of waste chemicals they will diffuse through the cell membrane out of the cell.
- When cells are surrounded by a low concentration of a nutrient then the nutrient will by moved by active transport through the cell membrane and into the cells.
- When a cell has filled with a low concentration of waste chemicals they will be moved by active transport through the cell membrane out of the cell.
About The Walls of the Alveoli as an Exchange Surface
- When air is inhaled into the lungs Oxygen diffuses from the air across the walls of the alveoli and into the red blood cells.
- Before air is exhaled out of the lungs Carbon Dioxide diffuses out of the blood through the walls of the alveoli and into air in the lungs.
- The walls of the alveoli have several adaptations to maximise the rate of diffusion across them:
- The alveoli have thin walls to allow gas exchange to happen quickly.
- Alveoli are in groups to make a large surface area in the lung for gas exchange.
- The alveoli have a good blood supply to allow gas exchange with the blood.
- The walls of the alveoli are kept moist to allow gases to dissolve into to the fluid for gas exchange with the blood.
About The Wall of the Small Intestines as an Exchange Surface
- When food is consumed and digested the nutrients can move across the walls of the small intestine into the blood stream by diffusion or active transport.
- The wall of the small intestine is adapted to allow the movement of nutrients from the food into the blood stream in the following ways:
- The small intestine is long to give it a large surface area.
- The wall of the small intestine is thin to provide a short distance for nutrients to travel from food to the blood stream.
- The wall of the small intestine is covered in villi which are small folds, also increasing the surface area.
- Villi have capillaries inside them for a good blood supply to allow for quick diffusion into the blood.
- Villi have a large surface area to allow quicker diffusion.
- The cells in the walls of the villi have microvilli to provide an even bigger surface area for quicker diffusion.
- The microvilli have extra mitochondria to provide energy for active transport.
References
AQA
- Exchange surfaces, pages 23-25, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Exchange surfaces, pages 54-56, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Exchange surfaces, pages 60-62, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Exchange surfaces, page 60, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Exchange surfaces, pages 257, 260, 261, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Exchange surfaces, pages 87, 88, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel