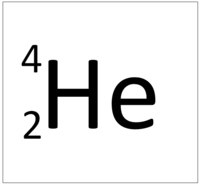Contents
Key Stage 3
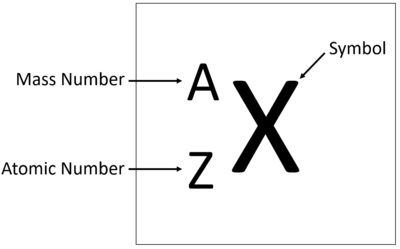
Meaning
The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
About The Atomic Number
- The Atomic Number of an atom determines which element it is.
- The number of protons also determines the number of electrons.
Examples
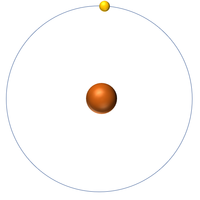
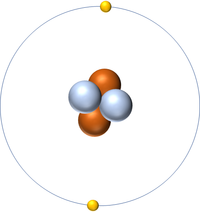
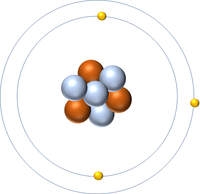
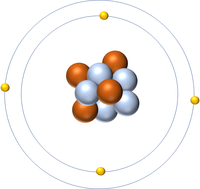
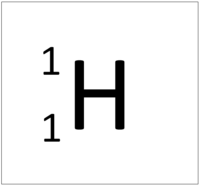
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| Hydrogen has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1. | Helium has 2 protons so its atomic number is 2. | Lithium has 3 protons so its atomic number is 3. | Beryllium has 4 protons so its atomic number is 4. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
About The Atomic Number
- The Atomic Number of an atom determines which element it is.
- Protons have a relative atomic charge of +1 so the number of protons determines the relative atomic charge of the atomic nucleus.
- The number of electrons orbiting the nucleus is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Examples
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| Hydrogen has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +1. | Helium has 2 protons so its atomic number is 2 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +2. | Lithium has 3 protons so its atomic number is 3 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +3. | Beryllium has 4 protons so its atomic number is 4 and the relative atomic charge of the nucleus is +4. |