Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
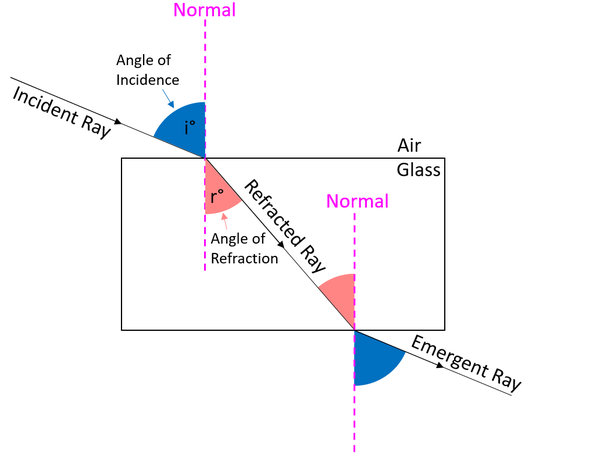
The angle of refraction is the angle between the between the refracted ray and the normal.
About the Angle of Refraction
- When light travels from air into glass the angle of refraction is always smaller than the angle of incidence.
- When light travels from glass into air the angle of refraction is always greater than the angle of incidence.
Examples
| The angle of incidence is highlighted in pale red in this diagram. |
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
The angle of refraction is the angle between the between the refracted ray and the normal.
About the Angle of Refraction
- When light travels from a less optically dense medium (such as air to a more optically dense medium (such as glass or water the angle of refraction is always smaller than the angle of incidence.
- When light travels from a more optically dense medium (such as glass or water) into a less optically dense medium (such as air) the angle of refraction is always greater than the angle of incidence.
Examples
| The angle of incidence is highlighted in pale red in this diagram. |