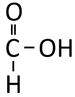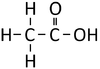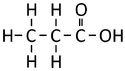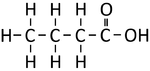Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Carboxylic Acids are organic compounds with a Carbon atom which has a double bonds to an Oxygen atom and a single bond to an OH group. The general formula is CnH2nO2.
About Carboxylic Acids
- Carboxylic Acids are a homologous series of organic compounds.
- The functional group of the Carboxylic Acids is the double bond between a Carbon atom and an Oxygen atom and the single bond to an OH group.
- Carboxylic Acids are long chains of Carbon atoms covalently bonded together with the the final Carbon atom in the chain as a COOH group.
Examples
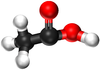
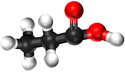
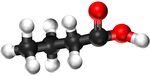
| Methanoic Acid | Ethanoic Acid | Propanoic Acid | Butanoic Acid | |
| Chemical Formula | CH2O2 | C2H4O2 | C3H6O2 | C4H8O2 |
| Structural Formula | HCOOH | CH3COOH | CH3CH2COOH | CH3CH2CH2COOH |
| Structural Diagram | ||||
| Ball and Stick Model |
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
Neutralisation
Carboxylic Acids can be neutralised to produce organic salts.
- Methanoic Acid + Potassium → Potassium Methanoate + Hydrogen
- <chem>2HCOOH + 2K -> 2HCOOK + H2</chem>
- Ethanoic Acid + Magnesium Oxide → Magnesium Ethanoate + Water
- <chem>2CH3COOH + MgO -> (CH3COO)2Mg + H2O</chem>
- Propanoic Acid + Sodium Hydroxide → Sodium Propanoate + Water
- <chem>C2H5COOH + NaOH -> C2H5COONa + H2O</chem>
- Butanoic Acid + Calcium Carbonate → Calcium Butanoate + Water + Carbon Dioxide
- <chem>2C3H7COOH + CaCO3 -> (C3H7COO)2Ca + H2O + CO2</chem>
Esterification
Carboxylic Acids may react with alcohols to produce compounds known as esters which have the functional group -COO-.
- Methanoic Acid + Ethanol → Ethyl Methanoate + Water
- <chem>HCOOH + C2H5OH -> HCOOC2H5 + H2O</chem>
- Ethanoic Acid + Ethanol → Ethyl Ethanoate + Water
- <chem>CH3COOH + C2H5OH -> CH3COOC2H5 + H2O</chem>
- Propanoic Acid + Propanol → Propyl Propanoate + Water
- <chem>C3H5COOH + C3H7OH -> C2H5COOC3H7 + H2O</chem>
- Butanoic Acid + Propanol → Propyl Butanoate + Water
- <chem>C3H5COOH + C3H7OH -> C3H5COOC3H7 + H2O</chem>