Key Stage 4
Meaning
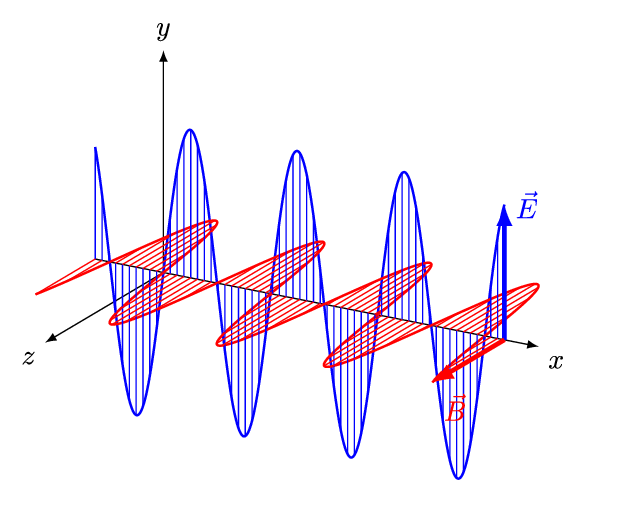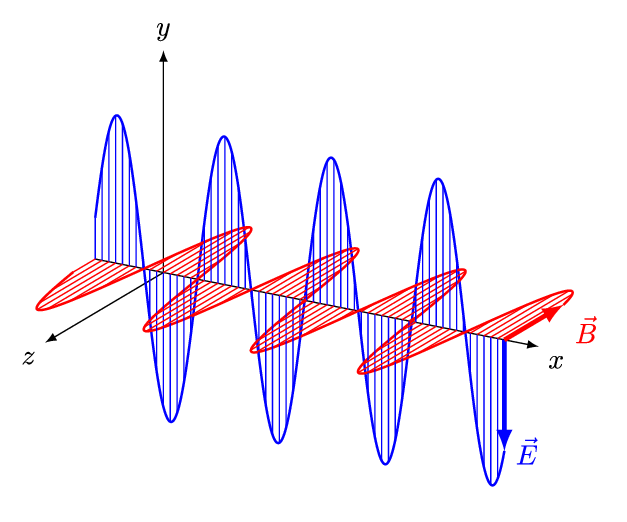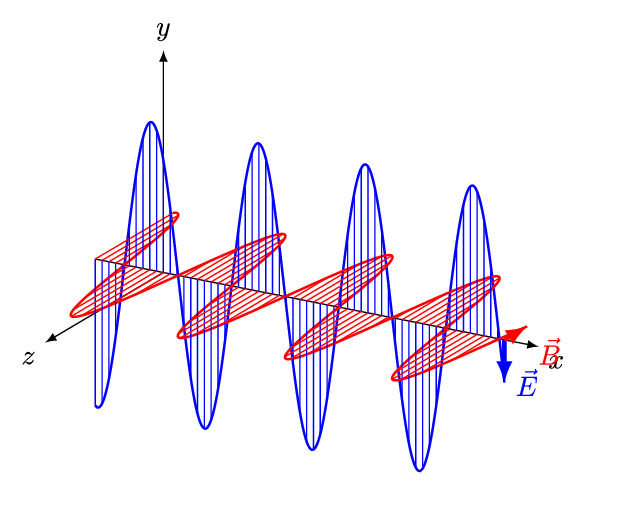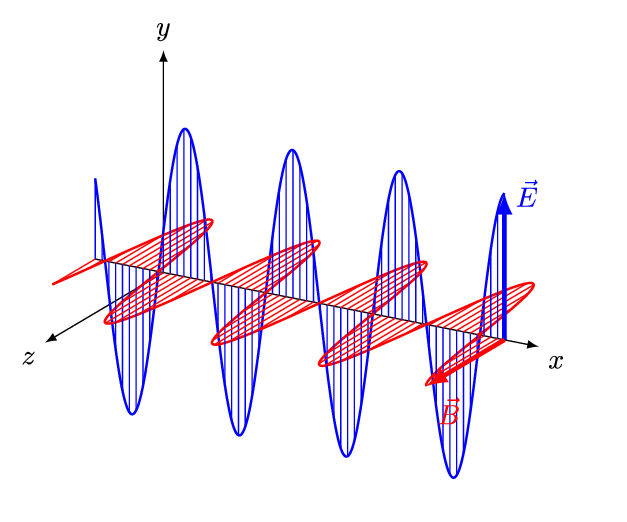
An electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave which transfers energy by oscillating electrostatic and magnetic fields.
About Electromagnetic Waves
- Electromagnetic waves are transverse because the oscillation of electrostatic and magnetic fields is perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.
- Electromagnetic waves, like all waves, carry energy and information but they do not transfer mass from one location to another.
- Electromagnetic waves can pass through any transparent medium.
- Electromagnetic waves do not need matter to be transmitted and can travel through a vacuum.
- All electromagntic waves travel at 300,000,000m/s through a vacuum.
- The properties of electromagntic waves depend on their frequency and wavelength. The lowest frequency transmits the least energy so they are the least dangerous. The highest frequency transmits the most energy so they are the most dangerous.
The electromagntic waves you should know in order from lowest frequency (longest wavelength) to highest frequency (shortest wavelength) are:
Properties
NB: You do not need to remember the exact frequency or wavelength but you should remember which are highest and lowest and put them in correct order.
Applications
| Electromagnetic Wave
|
Applications
|
| Radiowaves
|
Communication, radio broadcasts, television broadcasts.
|
| Microwaves
|
Communication, cooking food.
|
| Infrared
|
Remote controls, night vision, thermal imaging, cooking food.
|
| Visible Light
|
Sight, photography, microscopy, telescopy.
|
| Ultraviolet
|
Revealing fluorescent ink to detect forged bank notes, tanning beds.
|
| X-rays
|
Medical imaging of bones. Medical imaging of intestines, using Barium Sulphate, CAT scans to identify tumors.
|
| Gamma-rays
|
Sterilising food, sterilising medical equipment. Irradiating cancerous tumors.
|
Dangers
| Electromagnetic Wave
|
Dangers
|
| Radiowaves
|
No dangers.
|
| Microwaves
|
May cause internal heating.
|
| Infrared
|
Can cause skin burns.
|
| Visible Light
|
No dangers.
|
| Ultraviolet
|
Can cause sunburn and skin cancer by ionising and damaging DNA molecules leading to a mutation.
|
| X-rays
|
Can cause cancer anywhere in the body by ionising and damaging DNA molecules leading to a mutation.
|
| Gamma-rays
|
Can cause cancer anywhere in the body by ionising and damaging DNA molecules leading to a mutation. Can cause radiation poisoning with high exposure.
|