Difference between revisions of "Thermistor"
(→Key Stage 4) |
(→Description) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
====Description==== | ====Description==== | ||
| − | The | + | The [[IV Graph]] for an 'NTC' [[thermistor]] shows that: |
*At a high [[temperature]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] increases rapidly with the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] | *At a high [[temperature]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] increases rapidly with the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] | ||
*At a low [[temperature]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] increases slowly with the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]]. | *At a low [[temperature]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] increases slowly with the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]]. | ||
Revision as of 15:01, 28 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
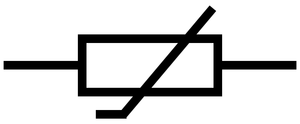
A thermistor is a resistor which changes resistance depending on the temperature.
About Thermistors
- 'NTC' thermistors decrease resistance as the temperature increases. (NTC = Negative Temperature Coefficient.)
- A thermistor can be used to control the current passing through a circuit. If the potential difference is constant then the current decreases as temperature decreases.
- A thermistor can be used to control the potential difference of another component in series with it. If the temperature is decreased then the potential difference across other components will decrease.
- Thermistors can be used temperature sensors.
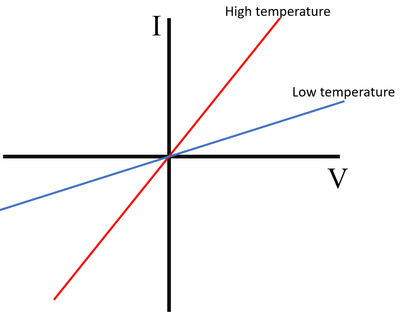
IV Graph
Description
The IV Graph for an 'NTC' thermistor shows that:
- At a high temperature the current increases rapidly with the potential difference
- At a low temperature the current increases slowly with the potential difference.
Explanation
- The resistance of an 'NTC' thermistor increases as the temperature decreases.