Difference between revisions of "Reflection"
(→The Law of Reflection) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[Reflection]] is when a wave bounces off a surface. | + | [[Reflection]] is when a [[wave]] bounces off a surface. |
===About Reflection=== | ===About Reflection=== | ||
: All [[wave]]s can be '''reflected'''. | : All [[wave]]s can be '''reflected'''. | ||
| − | : The [[reflection]] of [[sound]] is called an echo. | + | : The [[reflection]] of [[sound]] is called an [[echo]]. |
===The Law of Reflection=== | ===The Law of Reflection=== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
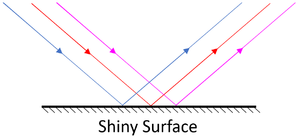
: [[Specular Reflection]] happens from a shiny surface and makes an [[image]] (you can see a 'reflection'). | : [[Specular Reflection]] happens from a shiny surface and makes an [[image]] (you can see a 'reflection'). | ||
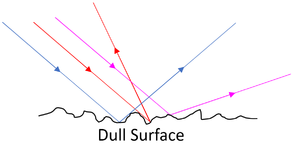
: [[Diffuse Reflection]] happens from a dull surface and is how we see all [[object]]s. | : [[Diffuse Reflection]] happens from a dull surface and is how we see all [[object]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:SpecularReflectionDiagram.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:DiffuseReflectionDiagram.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Specular Reflection]] happens from a smooth surface. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Diffuse Reflection]] happens from a rough surface. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[Reflection]] is when a [[wave]] bounces off the [[interface]] between two [[medium|media]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Reflection=== | ||
| + | : All [[wave]]s can be '''reflected''' (eg [[Light|Light Waves]], [[Water Wave]]s, [[Ultrasound|Ultrasound Wave]]s, [[X-ray]]s). | ||
| + | : [[Reflection]] takes place at the [[interface]] between two [[medium|media]]. | ||
| + | : The chance of [[reflection]] at an [[interface]] depends upon the relative [[property|properties]] of those two [[media]] and the [[Angle of Incidence]]. [[Wave]]s that arrive at an [[interface]] where there is a large difference in [[density]] or [[Refractive Index|refractive index]] are more likely to be '''reflected'''. | ||
| + | : The [[reflection]] of [[sound]] is called an [[echo]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Law of Reflection=== | ||
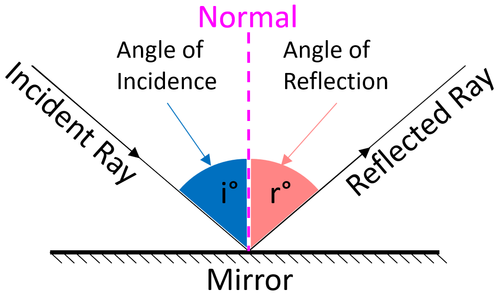
| + | : The Law of '''reflection''' states that the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]] is equal to the [[Angle of Reflection|angle of reflection]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ReflectionDiagram.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[angle]] between the [[Incident Ray|incident ray]] and the [[normal]] ([[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]) is the same as the [[angle]] between the [[Reflected Ray|reflected ray]] and the [[normal]] ([[Angle of Reflection|angle of reflection]]). | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Specular and Diffuse Reflection=== | ||
| + | : [[Reflection]] of [[Electromagntic Wave]]s can be [[Specular Reflection|specular]] or [[Diffuse Reflection|diffuse]]. | ||
| + | : [[Specular Reflection]] happens from a shiny, smooth surface and makes an [[image]]. | ||
| + | : [[Diffuse Reflection]] happens from a dull, rough surface sending the [[Reflected Ray|reflected rays]] in different directions. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 08:52, 19 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Reflection is when light bounces off a surface.
About Reflection
- Reflection can be specular or diffuse.
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny surface and makes an image (you can see a 'reflection').
- Diffuse Reflection happens from a dull surface and is how we see all objects.
| Specular Reflection from the glass makes an image of the sky in the glass. | Diffuse Reflection from the fabric is how light gets from the fabric to our eyes to see it. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Reflection is when a wave bounces off a surface.
About Reflection
- All waves can be reflected.
- The reflection of sound is called an echo.
The Law of Reflection
- The Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
| The angle between the incident ray and the normal (angle of incidence) is the same as the angle between the reflected ray and the normal (angle of reflection). |
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
- Reflection of light can be specular or diffuse.
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny surface and makes an image (you can see a 'reflection').
- Diffuse Reflection happens from a dull surface and is how we see all objects.
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. | Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Reflection is when a wave bounces off the interface between two media.
About Reflection
- All waves can be reflected (eg Light Waves, Water Waves, Ultrasound Waves, X-rays).
- Reflection takes place at the interface between two media.
- The chance of reflection at an interface depends upon the relative properties of those two media and the Angle of Incidence. Waves that arrive at an interface where there is a large difference in density or refractive index are more likely to be reflected.
- The reflection of sound is called an echo.
The Law of Reflection
- The Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
| The angle between the incident ray and the normal (angle of incidence) is the same as the angle between the reflected ray and the normal (angle of reflection). |
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
- Reflection of Electromagntic Waves can be specular or diffuse.
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny, smooth surface and makes an image.
- Diffuse Reflection happens from a dull, rough surface sending the reflected rays in different directions.
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. | Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface. |