Difference between revisions of "Polymer"
(→Meaning) |
(→About Polymers) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
: [[Polymer]]s are held together by [[Covalent Bond|covalent bonds]]. | : [[Polymer]]s are held together by [[Covalent Bond|covalent bonds]]. | ||
: The [[monomer]]s which make up a [[polymer]] are [[Simple Covalent Molecule|simple covalent molecules]]. | : The [[monomer]]s which make up a [[polymer]] are [[Simple Covalent Molecule|simple covalent molecules]]. | ||
| − | : Most [[polymer]]s are made of chains of [[Carbon]] [[atom]]s | + | : Most [[polymer]]s are made of chains of [[Carbon]] [[atom]]s since they can from up to 4 [[Covalent Bond|covalent bonds]] with [[adjacent]] [[atom]]s. However, some can be made from [[Silicon]], which can also form 4 [[Covalent Bond|covalent bond]]s. |
Revision as of 16:04, 27 December 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A polymer is a long molecule made by reacting together several smaller molecules.
About Polymers
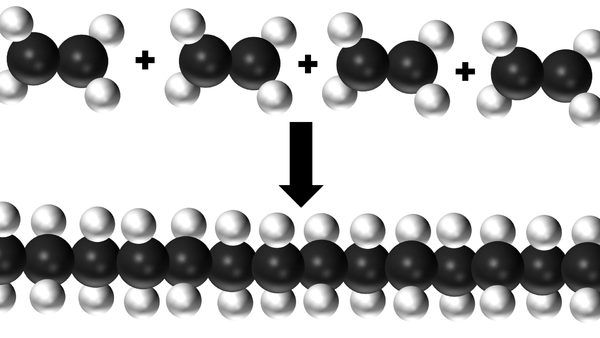
| This diagram shows several Ethene molecules reacting together to make a polythene molecule. |
Different polymers can have different properties but generally polymers are:
- Easily molded into shape.
- Solid at room temperature.
- Plastic in behaviour.
- An Electrical Insulator.
| Polymer | Properties | Application |
| Polythene | Plastic, Strong, Ductile | Shopping bags |
| PVC | Plastic, Electrical Insulator, Strong | Covering of electrical wires. |
| Nylon | Plastic, Strong, Flexible, Ductile. | Clothing |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A polymer is a large molecule made of many identical smaller molecules called monomers.
About Polymers
- Polymers are held together by covalent bonds.
- The monomers which make up a polymer are simple covalent molecules.
- Most polymers are made of chains of Carbon atoms since they can from up to 4 covalent bonds with adjacent atoms. However, some can be made from Silicon, which can also form 4 covalent bonds.