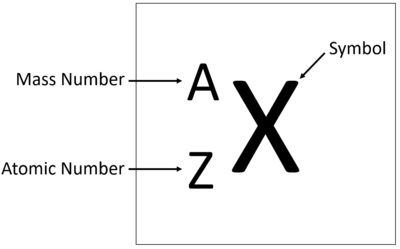
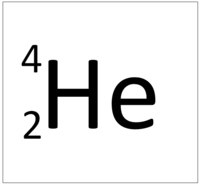Difference between revisions of "Atomic Number"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== right|400px|thumb|An [[element tile showing the Atomic Number.]] The Atomic Number is the number of protons...") |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Beryllium]] has 4 [[proton]]s so its '''atomic number''' is 4. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Beryllium]] has 4 [[proton]]s so its '''atomic number''' is 4. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[File:ElementTile.png|right|400px|thumb|An [[element]] tile showing the [[Atomic Number]].]] | ||
| + | The [[Atomic Number]] is the number of [[proton]]s in the [[nucleus]] of an [[atom]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About The Atomic Number=== | ||
| + | : The [[Atomic Number]] of an [[atom]] determines which [[element]] it is. | ||
| + | : [[Proton]]s have a [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of +1 so the number of [[proton]]s determines the [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative atomic charge]] of the [[Atomic Nucleus|atomic nucleus]]. | ||
| + | : The number of [[electron]]s [[orbit]]ing the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is the same as the number of [[proton]]s in the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] of an [[atom]]. | ||
Revision as of 18:59, 25 November 2018
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
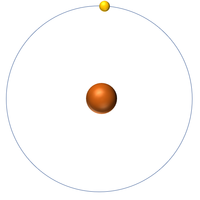
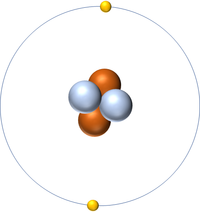
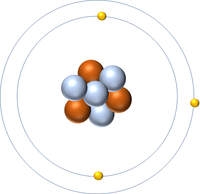
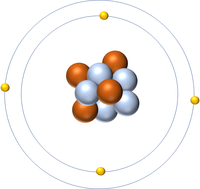
The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
About The Atomic Number
- The Atomic Number of an atom determines which element it is.
- The number of protons also determines the number of electrons.
Examples
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
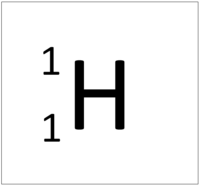
| Hydrogen has 1 proton so its atomic number is 1. | Helium has 2 protons so its atomic number is 2. | Lithium has 3 protons so its atomic number is 3. | Beryllium has 4 protons so its atomic number is 4. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Atomic Number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
About The Atomic Number
- The Atomic Number of an atom determines which element it is.
- Protons have a relative atomic charge of +1 so the number of protons determines the relative atomic charge of the atomic nucleus.
- The number of electrons orbiting the nucleus is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.