Difference between revisions of "Bohr Model"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== The Bohr Model is a model of the atom in which a positively charged nucleus is surrounded by ele...") |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
===About the Borh Model=== | ===About the Borh Model=== | ||
| − | : The [[Bohr Model]] was developed by [[Neils Bohr]] following observations that [[electron]]s could gain or lose specific amounts of [[energy]] with the [[Absorb (Physics)|absorption]] and [[Emit|emission]] of light. This suggested that there were specific [[Energy Level]]s that [[electron]]s could be in. | + | : The [[Bohr Model]] was developed by [[Neils Bohr]] following observations that [[electron]]s could gain or lose specific amounts of [[energy]] with the [[Absorb (Physics)|absorption]] and [[Emit|emission]] of light. This suggested that there were specific [[Energy Level]]s that [[electron]]s could be in. If an [[electron]] [[Absorb (Physics)|absorbs]] [[light]] it can move to a higher [[Energy Level|energy level]] and when it falls back to a lower [[Energy Level|energy level]] the [[electron]] will [[emit]] an [[electron]]. |
: These [[Electron Energy Level|energy levels]] are also referred to as [[Electron Orbital]]s and [[Electron Shell]]s. | : These [[Electron Energy Level|energy levels]] are also referred to as [[Electron Orbital]]s and [[Electron Shell]]s. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:BohrModel.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
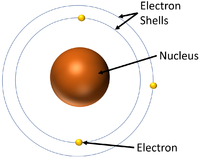
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of the [[Bohr Model]] with a [[Positive Charge|positively charged]] [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] in the centre and [[electron]]s [[orbit]]ing the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] in [[Energy Level|energy levels]] called 'shells'. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | : The [[Bohr Model]] was updated after the discovery of the [[neutron]] in 1932 by [[James Chadwick]]. The new version of the model included the [[proton]]s and [[neutron]]s within the [[nucleus]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:AtomDiagram.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
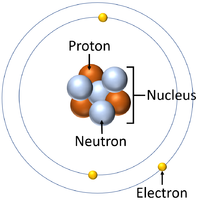
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of the updated [[Bohr Model]] which includes [[proton]]s and [[neutron]]s. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 24 November 2018
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Bohr Model is a model of the atom in which a positively charged nucleus is surrounded by electrons which orbit the nucleus in specific electron orbitals or 'shells'.
About the Borh Model
- The Bohr Model was developed by Neils Bohr following observations that electrons could gain or lose specific amounts of energy with the absorption and emission of light. This suggested that there were specific Energy Levels that electrons could be in. If an electron absorbs light it can move to a higher energy level and when it falls back to a lower energy level the electron will emit an electron.
- These energy levels are also referred to as Electron Orbitals and Electron Shells.
| A diagram of the Bohr Model with a positively charged nucleus in the centre and electrons orbiting the nucleus in energy levels called 'shells'. |
- The Bohr Model was updated after the discovery of the neutron in 1932 by James Chadwick. The new version of the model included the protons and neutrons within the nucleus.
| A diagram of the updated Bohr Model which includes protons and neutrons. |