Difference between revisions of "Diode"
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Diodes, page 229, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Diodes, page 229, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Diodes, page 388, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Diodes, page 388, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Diodes, pages 107, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Diodes, pages 176, 179, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945687/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945687&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a598e52189317a20311d7a632747bc9 ''Diodes, pages 45-47, Gateway GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:40, 4 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
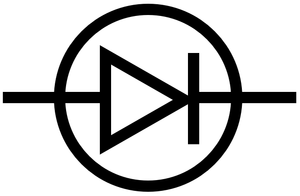
Meaning
A diode is an electrical component which only allows electricity through in one direction.
About Diodes
- Diodes have a low resistance in one direction but a very high resistance in the reverse direction.
- Diodes can be used to change an alternating current into a direct current.
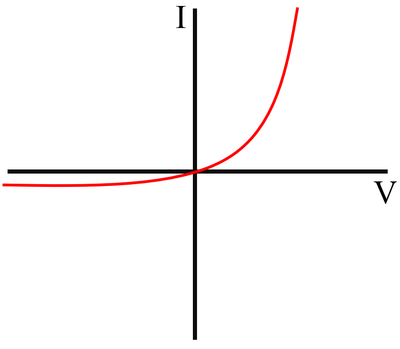
IV Graph
Description
The IV Graph for a diode shows that:
- For a positive potential difference the current increases rapidly with an increase in potential difference
- For a negative potential difference the current remains negligible and does not increase as the potential difference becomes larger.
Explanation
- The resistance of a diode is very low for current in the forward direction and very high in the back direction.
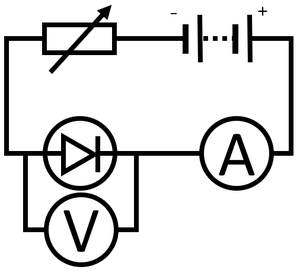
Obtaining the IV Graph
|
References
AQA
- Diode, pages 52-3, 65, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Diodes, page 43, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Diodes, pages 180, 181, 183, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Diodes, pages 24, 26, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Diodes, pages 293, 298, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Diodes, pages 52-53, 57, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Diodes, pages 60, 66, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Diodes, pages 62, 68, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Diodes; circuit symbol, page 38, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Diodes, page 148, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Diodes, page 229, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Diodes, page 388, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel