Difference between revisions of "Magnetic Flux Density"
(→Examples) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The '''magnetic flux density''' between two [[magnet]]s depends on the distance between those [[magnet]]s. The smaller the distance the greater the '''magnetic flux density'''. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The '''magnetic flux density''' between two [[magnet]]s depends on the distance between those [[magnet]]s. The smaller the distance the greater the '''magnetic flux density'''. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Magnetic flux density, page 222, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Magnetic flux density, page 296, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Magnetic flux density, pages 220-221, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Magnetic flux density, pages 280, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 10:08, 8 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Magnetic flux density is the strength of a magnetic field.
About Magnetic Flux Density
- The SI Unit of magnetic flux density is the Tesla (T).
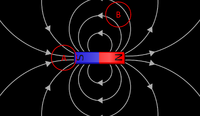
- Magnetic flux density is greatest at the poles of a magnet.
Examples
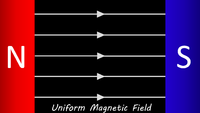
| The magnetic flux density is greatest at the poles of this bar magnet. | The magnetic flux density is the same everywhere in a uniform magnetic field. | The magnetic flux density between two magnets depends on the distance between those magnets. The smaller the distance the greater the magnetic flux density. |
References
AQA
- Magnetic flux density, page 222, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Magnetic flux density, page 296, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Magnetic flux density, pages 220-221, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Magnetic flux density, pages 280, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA