Difference between revisions of "Skin"
(→Key Stage 4) |
(→Key Stage 4) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
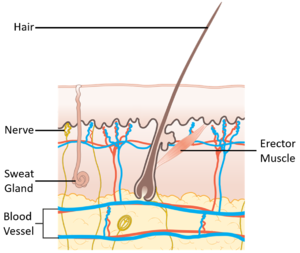
*[[Sweat Gland|Sweat glands]] on the [[skin]] [[secrete]] [[sweat]] which [[evaporate]]s from the [[skin]] cooling it down. | *[[Sweat Gland|Sweat glands]] on the [[skin]] [[secrete]] [[sweat]] which [[evaporate]]s from the [[skin]] cooling it down. | ||
*[[Erector Muscle|Erector muscles]] relax allowing the body hairs to lie flat on the [[skin]]. | *[[Erector Muscle|Erector muscles]] relax allowing the body hairs to lie flat on the [[skin]]. | ||
| − | *[[Blood Vessel|Blood vessels]] near the surface of the [[skin]] [[dilate]] to allow more of the warm [[blood]] to pass its [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy]] on to the [[skin]]. | + | *[[Blood Vessel|Blood vessels]] near the surface of the [[skin]] [[Vasodilation|dilate]] to allow more of the warm [[blood]] to pass its [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy]] on to the [[skin]]. |
When the [[Body Temperature|body temperature]] is too low: | When the [[Body Temperature|body temperature]] is too low: | ||
*[[Sweat Gland|Sweat glands]] stop [[secrete|secreting]] [[sweat]] and the [[skin]] becomes dry. | *[[Sweat Gland|Sweat glands]] stop [[secrete|secreting]] [[sweat]] and the [[skin]] becomes dry. | ||
*[[Erector Muscle|Erector muscles]] contract causing body hairs to stand on end. This creates a pocket of trapped air under the hairs which insulates the body. | *[[Erector Muscle|Erector muscles]] contract causing body hairs to stand on end. This creates a pocket of trapped air under the hairs which insulates the body. | ||
| − | *[[Blood Vessel|Blood vessels]] near the surface of the [[skin]] [[constrict]] reducing [[blood]] flow close to the [[skin]] preventing [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy]] being lost to the [[skin]]. | + | *[[Blood Vessel|Blood vessels]] near the surface of the [[skin]] [[Vasoconstriction|constrict]] reducing [[blood]] flow close to the [[skin]] preventing [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy]] being lost to the [[skin]]. |
==Beyond the Curriculum== | ==Beyond the Curriculum== | ||
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OxPlCkTKhzY}} | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OxPlCkTKhzY}} | ||
Revision as of 20:23, 24 June 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning

A picture of human skin with some hairs.
The skin is an organ covering the body.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The skin is an organ covering the body used to protect internal organs from infection.
About the Skin
- The skin has pigment called melanin that protects it from harsh sunlight.
- The skin is the largest organ of the human body.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The skin is an organ covering the body used to protect internal organs from infection.
About the Skin
- The skin has pigment called melanin that protects it from harsh sunlight.
- The skin is the largest organ of the human body.
- The skin is a physical barrier to prevent infection by pathogens.
- The skin is used in thermoregulation.
When the body temperature is too high:
- Sweat glands on the skin secrete sweat which evaporates from the skin cooling it down.
- Erector muscles relax allowing the body hairs to lie flat on the skin.
- Blood vessels near the surface of the skin dilate to allow more of the warm blood to pass its thermal energy on to the skin.
When the body temperature is too low:
- Sweat glands stop secreting sweat and the skin becomes dry.
- Erector muscles contract causing body hairs to stand on end. This creates a pocket of trapped air under the hairs which insulates the body.
- Blood vessels near the surface of the skin constrict reducing blood flow close to the skin preventing thermal energy being lost to the skin.