Difference between revisions of "Prokaryotic Cell"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
: '''Prokaryotic cells''' have no [[Cell Nucleus|nucleus]], [[mitochondria]] or [[chloroplast]]s. | : '''Prokaryotic cells''' have no [[Cell Nucleus|nucleus]], [[mitochondria]] or [[chloroplast]]s. | ||
: '''Prokaryotic cells''' are usually much smaller than [[Eukaryotic Cell|eukaryotic cells]]. | : '''Prokaryotic cells''' are usually much smaller than [[Eukaryotic Cell|eukaryotic cells]]. | ||
| − | + | : In the [[Three Domain System|three domain system]] '''prokaryotes''' include both [[bacteria]] and [[archae]]. | |
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 09:30, 23 June 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
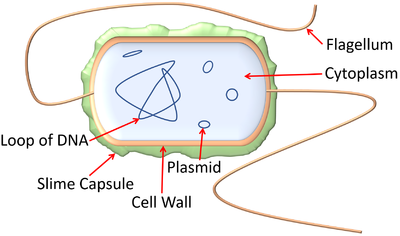
A prokaryotic cell is a simple cell which contains no membrane bound organelles.
About Prokaryotic Cells
- Prokaryotic cells include bacteria and some types of algae.
- Prokaryotic cells have a loop of DNA floating freely in the cytoplasm.
- Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus, mitochondria or chloroplasts.
- Prokaryotic cells are usually much smaller than eukaryotic cells.
- In the three domain system prokaryotes include both bacteria and archae.
Examples
| A diagram showing an E.coli bacterium which is a prokaryote. |