Difference between revisions of "Malaria"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
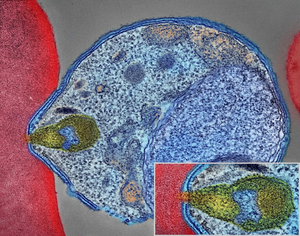
| + | [[File:Malaria.png|right|300px|thumb|A picture of the [[Pathogenic Protist|pathogenic protist]] '[[plasmodia]]' attached to a [[Red Blood Cell|red blood cell]].]] | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[Malaria]] is a [[disease]] caused by [[Pathogenic Protist|pathogenic protists]] called [[Plasmodia]]. | [[Malaria]] is a [[disease]] caused by [[Pathogenic Protist|pathogenic protists]] called [[Plasmodia]]. | ||
Revision as of 11:15, 6 June 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Malaria is a disease caused by pathogenic protists called Plasmodia.
About Malaria
- The malaria protist lives in the blood of humans and reproduces in the liver.
- Malaria can lay dormant, not causing any symptoms, for months at a time.
- Malaria causes fevers, liver damage and damage to the red blood cells.
- Malaria is transmitted by the mosquito which is referred to as a vector for the pathogen.
- Malaria is not easily treated and most people will have malaria for their entire lives.
The transmission of malaria can be prevented or reduced by:
- Killing mosquitos with insecticide.
- Destroying the habitat of the mosquito. (Areas of stagnant water.)
- Taking antimalarial drugs.
- Using mosquito nets that can be placed over beds.