Difference between revisions of "Consumer"
(→Examples) |
(→About Consumers) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
|[[File:FoodChain5.png|center|600px]] | |[[File:FoodChain5.png|center|600px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
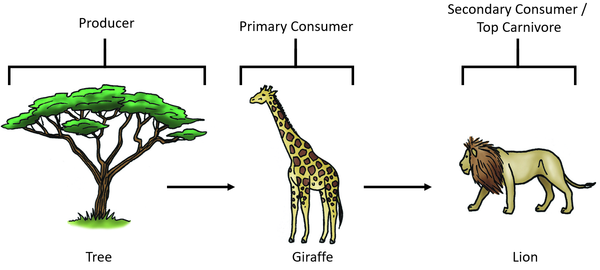
| − | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:center;" |In this [[Food Chain|food chain]] the [[giraffe]] is a primary [[consumer]] and the | + | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:center;" |In this [[Food Chain|food chain]] the [[giraffe]] is a primary [[consumer]] and the lion is a secondary [[consumer]]. |
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:FoodChain6.png|center|600px]] | |[[File:FoodChain6.png|center|600px]] | ||
Revision as of 20:38, 6 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A consumer is a creature the eats other creatures.
About Consumers
- A consumer cannot make its own food so it must eat other creatures.
- A consumer might eat a producer, or it might eat another consumer.
Examples
| In this food chain the bush is the producer and the gazelle and cheetah are consumers. |
| In this food chain the grass is the producer and the grasshopper, baboon and cheetah are all consumers. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A consumer is an organism that feeds off other organisms.
About Consumers
- A consumer cannot make its own food so it must eat other creatures.
- A consumer might eat a producer, or it might eat another consumer.
- Consumers can be labelled as primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary, depending on where they are in a food chain.
| In this food chain the giraffe is a primary consumer and the lion is a secondary consumer. |
| In this food chain the grasshopper, pied flycatcher, skunk and vulture are all consumers. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
About Consumers
- Consumers are in the second trophic level or higher.
- Consumers may be primary secondary, tertiary or quaternary consumers.
- Consumers are usually either animals or fungi.