Difference between revisions of "Range"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===About Range=== | ===About Range=== | ||
: The [[range]] is found by [[repeat]]ing the same [[reading]] or [[measurement]] and subtracting the smallest value from the largest value. | : The [[range]] is found by [[repeat]]ing the same [[reading]] or [[measurement]] and subtracting the smallest value from the largest value. | ||
| − | : The [[range]] is useful to calculate the [[uncertainty]] in a [[reading]] or [[measurement]] by dividing it by 2.<math>Uncertainty=\frac{range}{2}</math>. | + | : The [[range]] is useful to calculate the [[uncertainty]] in a [[reading]] or [[measurement]] by dividing it by 2. |
| + | |||
| + | <math>Uncertainty=\frac{range}{2}</math>. | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
Revision as of 13:02, 6 April 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The range is the difference between the highest and lowest value obtained during the repeat of the same measurement.
About Range
- The range is found by repeating the same reading or measurement and subtracting the smallest value from the largest value.
- The range is useful to calculate the uncertainty in a reading or measurement by dividing it by 2.
\(Uncertainty=\frac{range}{2}\).
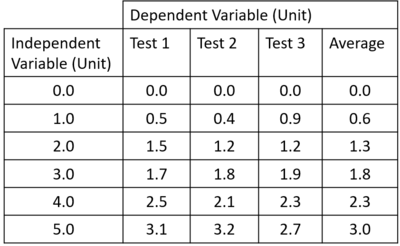
Examples
| The range is found by subtracting the smallest from the largest value.
The ranges in this results table are: 0 0.5 0.3 0.2 0.4 0.5 |