Difference between revisions of "Angle of Refraction"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
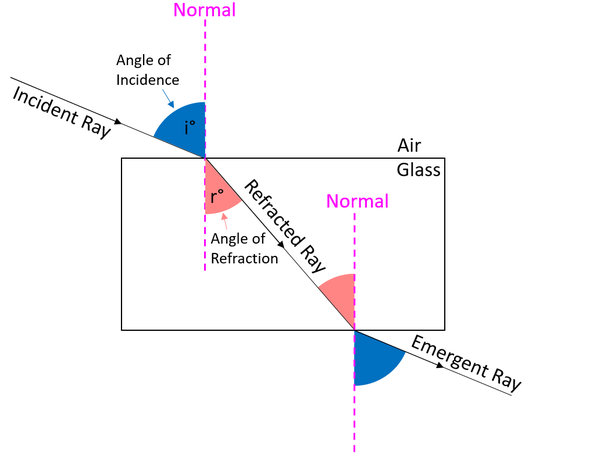
The '''angle of refraction''' is the [[angle]] between the between the [[Refracted Ray|refracted ray]] and the [[normal]]. | The '''angle of refraction''' is the [[angle]] between the between the [[Refracted Ray|refracted ray]] and the [[normal]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About the Angle of Refraction=== | ||
| + | : When [[light]] travels from [[air]] into [[glass]] the '''angle of refraction''' is always smaller than the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]. | ||
| + | : When [[light]] travels from [[glass]] into [[air]] the '''angle of refraction''' is always greater than the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:RefractionGlassBlock.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;"|The '''angle of incidence''' is highlighted in pale red in this [[diagram]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4 Higher== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | The '''angle of refraction''' is the [[angle]] between the between the [[Refracted Ray|refracted ray]] and the [[normal]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About the Angle of Refraction=== | ||
| + | : When [[light]] travels from a less [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] (such as [[air]] to a more [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] (such as [[glass]] or [[water]] the '''angle of refraction''' is always smaller than the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]. | ||
| + | : When [[light]] travels from a more [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] (such as [[glass]] or [[water]]) into a less [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] (such as [[air]]) the '''angle of refraction''' is always greater than the [[Angle of Incidence|angle of incidence]]. | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
Revision as of 09:50, 4 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The angle of refraction is the angle between the between the refracted ray and the normal.
About the Angle of Refraction
- When light travels from air into glass the angle of refraction is always smaller than the angle of incidence.
- When light travels from glass into air the angle of refraction is always greater than the angle of incidence.
Examples
| The angle of incidence is highlighted in pale red in this diagram. |
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
The angle of refraction is the angle between the between the refracted ray and the normal.
About the Angle of Refraction
- When light travels from a less optically dense medium (such as air to a more optically dense medium (such as glass or water the angle of refraction is always smaller than the angle of incidence.
- When light travels from a more optically dense medium (such as glass or water) into a less optically dense medium (such as air) the angle of refraction is always greater than the angle of incidence.
Examples
| The angle of incidence is highlighted in pale red in this diagram. |