Difference between revisions of "GCSE Physics Required Practical: Calculating Densities"
(→Improving Accuracy) |
(→Method) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:RequiredPracticalDensity2.png|center|400px]] |
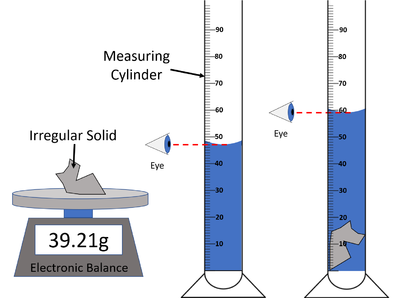
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of the [[apparatus]] used in an [[experiment]] to find the [[density]] of an irregular [[solid]]. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of the [[apparatus]] used in an [[experiment]] to find the [[density]] of an irregular [[solid]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 15:19, 20 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Finding the density of solid objects.
Experiment 1: Regular Cuboid
Method
| A diagram of the apparatus used in an experiment to find the density of a regular cuboid. |
- Measure the mass of the cuboid using an electronic balance or measuring scale.
- Measure the length, width and height of the cuboid using a ruler.
- Multiply the length, width and height to calculate the volume.
- Use the equation \(\rho = \frac{m}{V}\) to calculate the density of the cuboid.
Improving Precision
- Use a ruler with a higher resolution.
- Use an electronic balance with a higher resolution.
- Use a larger cuboid to reduce the uncertainty caused by the resolution of the measuring devices.
Experiment 1: Irregular Solid
Method
| A diagram of the apparatus used in an experiment to find the density of an irregular solid. |
- Measure the mass of the object using an electronic balance or measuring scale.
- Fill a measuring cylinder with enough water to submerse the object.
- Take a reading of the volume of water in the Measuring Cylinder.
- Place the object in the Measuring Cylinder and ensure it is submersed.
- Take a reading of the volume of water + object in the Measuring Cylinder.
- Subtract the volume of water from the volume of water + object to find the volume of the object.
- Use the equation \(\rho = \frac{m}{V}\) to calculate the density of the irregular object.
Improving Accuracy
- Ensure the mass is measured at the start of the experiment so that the mass is measured while the object is dry.
Improving Precision
- Use an electronic balance with a higher resolution.