Difference between revisions of "Gravity"
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
*[[Distance]] - The greater the distance between [[object]]s the weaker the [[force]] of [[gravity]]. | *[[Distance]] - The greater the distance between [[object]]s the weaker the [[force]] of [[gravity]]. | ||
: When a small [[mass]] [[object]] is in the [[Gravitational Field]] of a large [[mass]] [[object]] the [[force]] on the small [[mass]] is referred to as [[weight]] rather than [[gravity]]. | : When a small [[mass]] [[object]] is in the [[Gravitational Field]] of a large [[mass]] [[object]] the [[force]] on the small [[mass]] is referred to as [[weight]] rather than [[gravity]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ForcesEqual.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
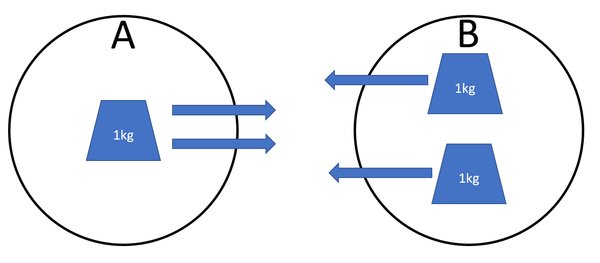
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Object]] A has 1[[kg]] of [[mass]] and is [[attract]]ed to [[object]] B. [[Object]] B has 2[[kg]] of [[mass]] and is [[attract]]ed to [[object]] A. The [[force]] acting on [[object]] A is the same as the [[force]] on [[object]] B. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Falling=== | ||
| + | ====Energy Transfers==== | ||
| + | =====Accelerating===== | ||
| + | : When an [[object]] [[accelerate]]s towards the ground [[energy]] is [[Energy Transfer|transferred]] from the [[Gravitational Potential Energy Store|gravitational potential energy store]] of the [[object]] to the [[Kinetic Energy Store|kinetic energy store]] of the [[object]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Decelerating===== | ||
| + | : When an [[object]] [[decelerate]]s away from the ground [[energy]] is [[Energy Transfer|transferred]] from the [[Kinetic Energy Store|kinetic energy store]] of the [[object]] to the [[Gravitational Potential Energy Store|gravitational potential energy store]] of the [[object]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Forces==== | ||
| + | =====Accelerating===== | ||
| + | : When an [[object]] [[accelerate]]s towards the ground '''gravity''' is causing a [[Mechanical Energy Transfer|mechanical energy transfer]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====Decelerating===== | ||
| + | : When an [[object]] [[decelerate]]s away from the ground '''gravity''' is causing a [[Mechanical Energy Transfer|mechanical energy transfer]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Orbits=== | ||
| + | : [[Isaac Newton|Newton]] was the first person to realise that [[object]]s were held in [[orbit]] by [[gravity]] which he [[explain]]ed in his [[Newton's Universal Theory of Gravitation|Universal Theory of Gravitation]]. | ||
| + | : [[Moon]]s [[orbit]] [[planet]]s and [[planet]]s [[orbit]] the [[stars]] due to [[gravity]]. | ||
| + | : [[Gravity]] is a constant [[force]] directed to the centre of a [[massive]] [[object]]. | ||
| + | : [[The Moon]] feels a [[force]] pulling it towards the centre of the [[Earth]]. The [[Earth]] feels a [[force]] equal in [[magnitude]] but opposite in direction to that of [[The Moon]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:Orbit1.gif|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
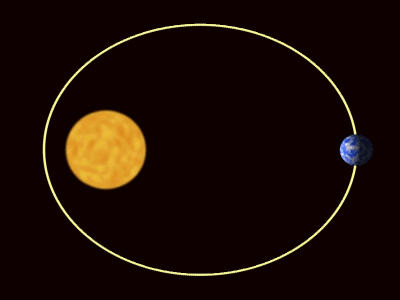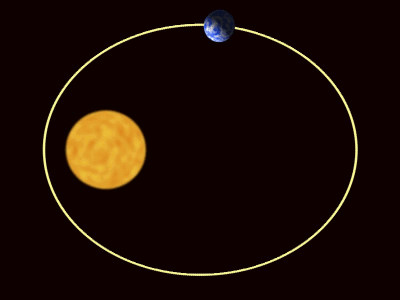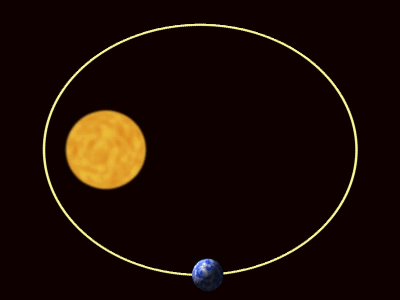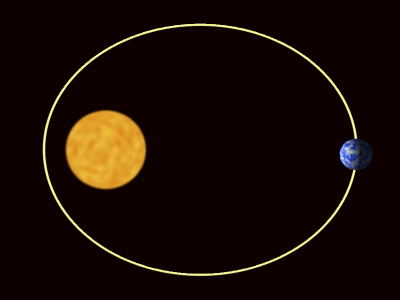
| + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:center;" |The [[planet]]s are pulled towards [[The Sun]] by [[gravity]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 08:58, 12 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Gravity is a force that causes all objects to be attracted to each other.
About Gravity
- Gravity is a non-contact force.
- Gravity affects all objects.
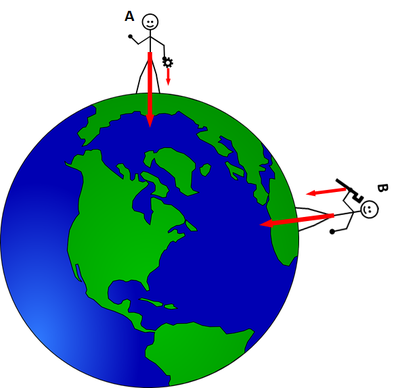
- Gravity pulls us down towards the centre of the Earth.
| If person A drops the cog it will fall towards the centre of the Earth. If person B drops the spanner it will fall towards the centre of the Earth. |
| The planets are pulled towards the The Sun by gravity. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Gravity is a force that causes all objects with mass to be attracted to each other.
About Gravity
- Gravity is a force so it is measured in Newtons.
- Gravity is a non-contact force because it can act without objects touching.
- All objects are affected by gravity.
- Gravity is the force that pulls objects to the ground.
- Isaac Newton was the first to realise that gravity is the force that holds the planets in orbit around The Sun.
- The force of gravity between two objects is always equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
| Object A has 1kg of mass and is attracted to object B. Object B has 2kg of mass and is attracted to object A. The force acting on object A is the same as the force on object B. |
Falling
Energy Transfers
Accelerating
- When an object accelerates towards the ground energy is transferred from the gravitational potential energy store of the object to the kinetic energy store of the object.
Decelerating
- When an object decelerates away from the ground energy is transferred from the kinetic energy store of the object to the gravitational potential energy store of the object.
Forces
Accelerating
- When an object accelerates towards the ground gravity is causing a mechanical energy transfer.
Decelerating
- When an object decelerates away from the ground gravity is causing a mechanical energy transfer.
Orbits
- Newton was the first person to realise that objects were held in orbit by gravity which he explained in his Universal Theory of Gravitation.
- Moons orbit planets and planets orbit the stars due to gravity.
- Gravity is a constant force directed to the centre of a massive object.
- The Moon feels a force pulling it towards the centre of the Earth. The Earth feels a force equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to that of The Moon.
| The planets are pulled towards The Sun by gravity. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Gravity is a force of attraction which acts between all objects with mass.
About Gravity
The strength of gravity between two objects depends on:
- Mass - The greater the mass of the objects the greater the force of gravity.
- Distance - The greater the distance between objects the weaker the force of gravity.
- When a small mass object is in the Gravitational Field of a large mass object the force on the small mass is referred to as weight rather than gravity.
| Object A has 1kg of mass and is attracted to object B. Object B has 2kg of mass and is attracted to object A. The force acting on object A is the same as the force on object B. |
Falling
Energy Transfers
Accelerating
- When an object accelerates towards the ground energy is transferred from the gravitational potential energy store of the object to the kinetic energy store of the object.
Decelerating
- When an object decelerates away from the ground energy is transferred from the kinetic energy store of the object to the gravitational potential energy store of the object.
Forces
Accelerating
- When an object accelerates towards the ground gravity is causing a mechanical energy transfer.
Decelerating
- When an object decelerates away from the ground gravity is causing a mechanical energy transfer.
Orbits
- Newton was the first person to realise that objects were held in orbit by gravity which he explained in his Universal Theory of Gravitation.
- Moons orbit planets and planets orbit the stars due to gravity.
- Gravity is a constant force directed to the centre of a massive object.
- The Moon feels a force pulling it towards the centre of the Earth. The Earth feels a force equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to that of The Moon.
| The planets are pulled towards The Sun by gravity. |