Difference between revisions of "Diode"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
: [[Diode]]s can be used to change an [[Alternating Current|alternating current]] into a [[Direct Current|direct current]]. | : [[Diode]]s can be used to change an [[Alternating Current|alternating current]] into a [[Direct Current|direct current]]. | ||
| + | ===IV Graph=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|[[File:IVGraphDiode.png|center|400px]] | |[[File:IVGraphDiode.png|center|400px]] | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
====Description==== | ====Description==== | ||
| − | The | + | The [[IV Graph]] for a [[diode]] shows that: |
*For a positive [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] increases rapidly with an increase in [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] | *For a positive [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] increases rapidly with an increase in [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] | ||
*For a negative [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] remains negligible and does not increase as the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] becomes larger. | *For a negative [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] remains negligible and does not increase as the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] becomes larger. | ||
Revision as of 14:56, 28 February 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A diode is an electrical component which only allows electricity through in one direction.
About Diodes
- Diodes have a low resistance in one direction but a very high resistance in the reverse direction.
- Diodes can be used to change an alternating current into a direct current.
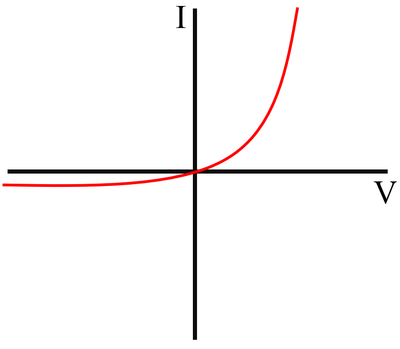
IV Graph
Description
The IV Graph for a diode shows that:
- For a positive potential difference the current increases rapidly with an increase in potential difference
- For a negative potential difference the current remains negligible and does not increase as the potential difference becomes larger.