Difference between revisions of "Electrical Insulator"
(→About Electrical Conductors) |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
: To determine if an [[object]] is a good '''electrical insulator''' the [[object]] can be added to a [[circuit]]. If a [[Electrical Current|current]] flows then it is not a good '''insulator'''. | : To determine if an [[object]] is a good '''electrical insulator''' the [[object]] can be added to a [[circuit]]. If a [[Electrical Current|current]] flows then it is not a good '''insulator'''. | ||
: To compare the effectiveness of different '''insulators''' an [[ammeter]] can be added to the [[circuit]]. The higher the [[Electrical Current|current]] the worse the [[object]] is at '''insulating'''. | : To compare the effectiveness of different '''insulators''' an [[ammeter]] can be added to the [[circuit]]. The higher the [[Electrical Current|current]] the worse the [[object]] is at '''insulating'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | An '''electrical insulator''' is a [[material]] with a very high [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] to the flow of [[electricity]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Electrical Conductors=== | ||
| + | : [[Non-metal]] [[element]]s are usually good '''electrical insulators''' as [[electron]]s are not free to move from one [[atom]] to another. [[Carbon]] in the form of [[graphite]] is an exception to this. | ||
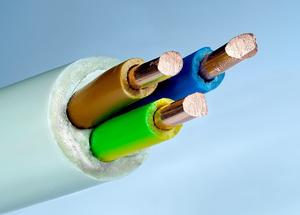
| + | : [[Plastic (Material)|Plastic]]s are good '''insulators''' because [[Covalent Bond|covalent bonds]] share [[electron]]s but do not allow [[electron]]s to be transferred from one [[atom]] to another. | ||
| + | : [[Metal]] [[element]]s are poor '''electrical insulators'''. | ||
| + | : To determine if an [[object]] is a good '''electrical insulator''' the [[object]] can be added to a [[circuit]]. If the [[ratio]] of [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] to [[Electrical Current|current]] is high then it is a good '''insulator'''. | ||
Revision as of 20:26, 25 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
An electrical insulator is a material that does not allow electricity to flow through it easily.
- Singular Noun: Electrical insulator
- Plural Noun: Electrical insulator
- Verb: To electrically insulate
- Adjective: Electrical insulation
About Electrical Conductors
| Brick is a good electrical insulator. | Fabric is a good electrical insulator. | Glass is a good electrical insulator. |
| Plastic is a good electrical insulator. | Rock is a good electrical insulator. | Rubber is a good electrical insulator. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An electrical insulator is a material with a very high resistance to the flow of electricity.
About Electrical Conductors
- Non-metal elements are usually good electrical insulators. Carbon in the form of graphite is an exception to this.
- Metal elements are poor electrical insulators.
- To determine if an object is a good electrical insulator the object can be added to a circuit. If a current flows then it is not a good insulator.
- To compare the effectiveness of different insulators an ammeter can be added to the circuit. The higher the current the worse the object is at insulating.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An electrical insulator is a material with a very high resistance to the flow of electricity.
About Electrical Conductors
- Non-metal elements are usually good electrical insulators as electrons are not free to move from one atom to another. Carbon in the form of graphite is an exception to this.
- Plastics are good insulators because covalent bonds share electrons but do not allow electrons to be transferred from one atom to another.
- Metal elements are poor electrical insulators.
- To determine if an object is a good electrical insulator the object can be added to a circuit. If the ratio of potential difference to current is high then it is a good insulator.