Difference between revisions of "Reflection"
(→Specular and Diffuse Reflection) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|[[File:Fabric.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:Fabric.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Specular Reflection]] from the [[glass]] makes an [[image]] of the | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Specular Reflection]] from the [[glass]] makes an [[image]] of the sky in the [[glass]]. |
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Diffuse Reflection]] from the [[fabric]] is how [[light]] gets from the [[fabric]] to our [[eyes]] to see it. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Diffuse Reflection]] from the [[fabric]] is how [[light]] gets from the [[fabric]] to our [[eyes]] to see it. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
: [[Reflection]] takes place at the [[interface]] between two [[medium|media]]. | : [[Reflection]] takes place at the [[interface]] between two [[medium|media]]. | ||
: For [[opaque]] [[material]]s [[reflection]] depends on the [[colour]] of the [[material]]. Rough [[opaque]] [[material]]s such as paper will [[Diffuse Reflection|diffusely reflect]] and smooth [[opaque]] [[material]]s will [[Specular Reflection|specularly reflect]] such as [[metal]]s. | : For [[opaque]] [[material]]s [[reflection]] depends on the [[colour]] of the [[material]]. Rough [[opaque]] [[material]]s such as paper will [[Diffuse Reflection|diffusely reflect]] and smooth [[opaque]] [[material]]s will [[Specular Reflection|specularly reflect]] such as [[metal]]s. | ||
| − | : For [[transparent]] [[material]]s the chance of [[reflection]] at an [[interface]] depends upon the relative [[property|properties]] of those two [[media]] and the [[Angle of Incidence]]. [[Wave]]s that arrive at an [[interface]] where there is a large difference in [[density]] or [[Refractive Index|refractive index]] are more likely to be '''reflected'''. | + | : For [[transparent]] [[material]]s the chance of [[reflection]] at an [[interface]] depends upon the relative [[property|properties]] of those two [[medium|media]] and the [[Angle of Incidence]]. [[Wave]]s that arrive at an [[interface]] where there is a large difference in [[density]] or [[Refractive Index|refractive index]] are more likely to be '''reflected'''. |
: [[Electromagnetic Wave|Electromagnetic waves]] travelling through a more [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] will engage in [[Total Internal Reflection|total internal reflection]] at the [[interface]] with a less [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]]. | : [[Electromagnetic Wave|Electromagnetic waves]] travelling through a more [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]] will engage in [[Total Internal Reflection|total internal reflection]] at the [[interface]] with a less [[Optical Density|optically dense]] [[medium]]. | ||
Revision as of 09:53, 4 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Reflection is when light bounces off a surface.
About Reflection
- Reflection can be specular or diffuse.
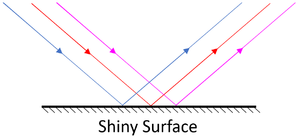
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny surface and makes an image (you can see a 'reflection').
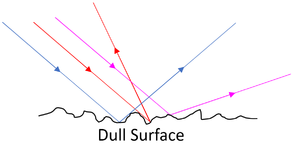
- Diffuse Reflection happens from a dull surface and is how we see all objects.
| Specular Reflection from the glass makes an image of the sky in the glass. | Diffuse Reflection from the fabric is how light gets from the fabric to our eyes to see it. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Reflection is when a wave bounces off a surface.
About Reflection
- All waves can be reflected.
- The reflection of sound is called an echo.
The Law of Reflection
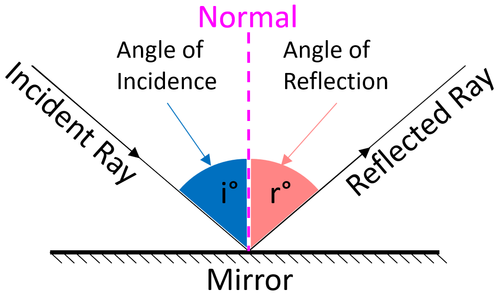
- The Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
| The angle between the incident ray and the normal (angle of incidence) is the same as the angle between the reflected ray and the normal (angle of reflection). |
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
- Reflection of light can be specular or diffuse.
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny surface and makes an image (you can see a 'reflection').
- Diffuse Reflection happens from a dull surface and is how we see all objects.
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. | Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Reflection is when a wave bounces off the interface between two media.
About Reflection
- All waves can be reflected (eg Light Waves, Water Waves, Ultrasound Waves, X-rays).
- Reflection takes place at the interface between two media.
- For opaque materials reflection depends on the colour of the material. Rough opaque materials such as paper will diffusely reflect and smooth opaque materials will specularly reflect such as metals.
- For transparent materials the chance of reflection at an interface depends upon the relative properties of those two media and the Angle of Incidence. Waves that arrive at an interface where there is a large difference in density or refractive index are more likely to be reflected.
- Electromagnetic waves travelling through a more optically dense medium will engage in total internal reflection at the interface with a less optically dense medium.
The Law of Reflection
- The Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
| The angle between the incident ray and the normal (angle of incidence) is the same as the angle between the reflected ray and the normal (angle of reflection). |
Specular and Diffuse Reflection
- Reflection of Electromagnetic Waves can be specular or diffuse.
- Specular Reflection happens from a shiny, smooth surface and makes an image.
- Diffuse Reflection happens from a dull, rough surface sending the reflected rays in different directions.
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. | Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface. |