Difference between revisions of "Circular Motion"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== '''Circular motion''' is when an object travels in a circular path due to a constant force acting towards the centre of that circular pat...") |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
: An [[object]] will move in straight line unless a [[force]] acts to [[accelerate]] the [[object]] to change its direction. | : An [[object]] will move in straight line unless a [[force]] acts to [[accelerate]] the [[object]] to change its direction. | ||
: '''Circular motion''' is caused by a constant [[force]] acting towards a point. | : '''Circular motion''' is caused by a constant [[force]] acting towards a point. | ||
| − | : An [[object]] following '''circular motion''' has a constant [[speed]] but does not have a constant [[velocity]]. | + | : An [[object]] following '''circular motion''' has a constant [[speed]] (a [[scalar]]) but does not have a constant [[velocity]] (a [[vector]]) as it is changing direction. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 15:20, 13 February 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
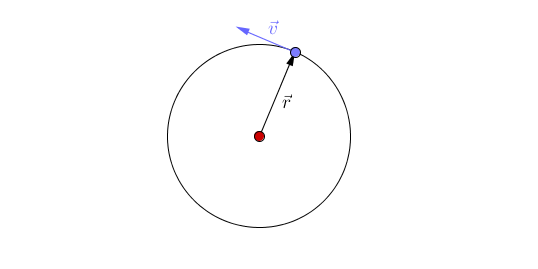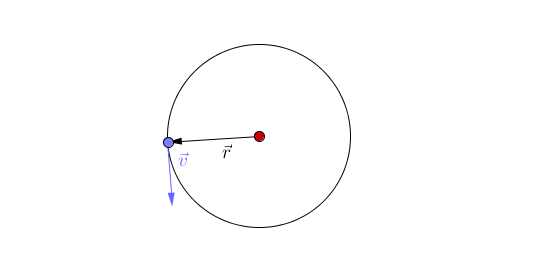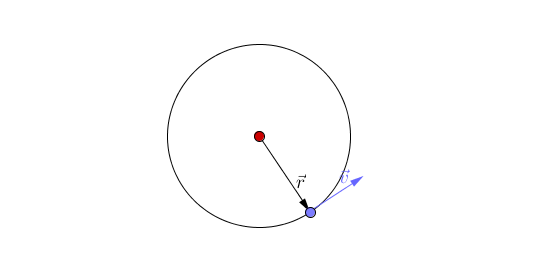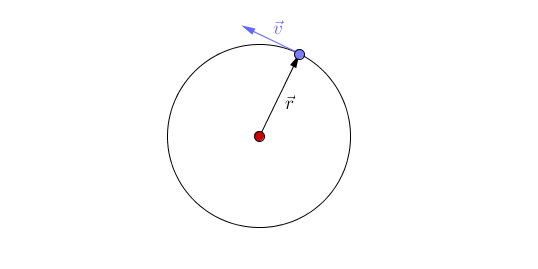
Circular motion is when an object travels in a circular path due to a constant force acting towards the centre of that circular path.
About Circular Motion
- An object will move in straight line unless a force acts to accelerate the object to change its direction.
- Circular motion is caused by a constant force acting towards a point.
- An object following circular motion has a constant speed (a scalar) but does not have a constant velocity (a vector) as it is changing direction.
| This animation shows the circular motion of an object due to a force pulling it towards the centre of the circle. The velocity is constantly changing even though the speed is constant. It is accelerating due to the force pulling it towards the centre. |