Difference between revisions of "Upthrust"
(→Calculating Upthrust) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
''NB: You don not need to remember this equation.'' | ''NB: You don not need to remember this equation.'' | ||
| − | + | Pressure = (Density of the fluid) x (Gravitational Field Strength) x (Depth) | |
| − | <math> | + | <math> P = \rho g h</math> |
Where: | Where: | ||
| − | <math> | + | <math> P</math> = [[Pressure]] caused by the [[fluid]]. |
<math>\rho</math> = [[Density]] of [[fluid]]. | <math>\rho</math> = [[Density]] of [[fluid]]. | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
<math>g</math> = [[Gravitational Field Strength]] | <math>g</math> = [[Gravitational Field Strength]] | ||
| − | <math>h</math> = [[ | + | <math>h</math> = [[Depth]] of the [[object]] in the [[fluid]]. |
| + | |||
| + | '' '''Upthrust''' = (Difference in pressure between top and bottom) x (Cross sectional area perpendicular to depth) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> F_u = \delta P A</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> F_u</math> = The [[force]] of [[upthrust]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> \delta P</math> = [[Pressure]] difference between the top and bottom of the [[object]]. | ||
<math>A</math> = [[Cross Sectional Area|Cross sectional area]] of the [[object]] [[perpendicular]] to the [[height]]. | <math>A</math> = [[Cross Sectional Area|Cross sectional area]] of the [[object]] [[perpendicular]] to the [[height]]. | ||
Revision as of 11:24, 11 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
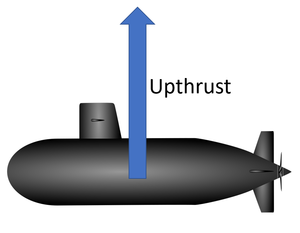
Upthrust is a force that acts upwards in a fluid due to the fluid being displaced.
About Upthrust
- Upthrust is a force so it is measured in Newtons.
- The force of upthrust is equal to the weight of fluid that has been displaced by an object.
- An object in the water experiences more upthrust than an object in air because water is more dense than air.
- Upthrust is weak in the air because the air is not very dense. For most objects in air upthrust can be ignored because it is so small.
- Upthrust is caused by the pressure in a fluid. Pressure increases with depth so the bottom of an object will experience more pressure than the top. This difference in pressure results in a difference between the force on the bottom and the top, known as upthrust.
Examples
| A boat floats on the water because the weight is balanced by the upthrust. | A submarine can change the amount of upthrust in order to rise or sink in the water. |
Key Stage 4 Foundation
Meaning
Upthrust is a force that acts upwards in a fluid due to the fluid being displaced.
About Upthrust
- Upthrust is a force so it is measured in Newtons.
- The force of upthrust is equal to the weight of fluid that has been displaced by an object.
- An object in the water experiences more upthrust than an object in air because water is more dense than air.
- Upthrust is weak in the air because the air is not very dense. For most objects in air upthrust can be ignored because it is so small.
- Upthrust is caused by the pressure in a fluid. Pressure increases with depth so the bottom of an object will experience more pressure than the top. This difference in pressure results in a difference between the force on the bottom and the top, known as upthrust.
Key Stage 4 Higher
Calculating Upthrust
NB: You don not need to remember this equation.
Pressure = (Density of the fluid) x (Gravitational Field Strength) x (Depth)
\( P = \rho g h\)
Where\[ P\] = Pressure caused by the fluid.
\(g\) = Gravitational Field Strength
\(h\) = Depth of the object in the fluid.
Upthrust = (Difference in pressure between top and bottom) x (Cross sectional area perpendicular to depth)
\( F_u = \delta P A\)
Where\[ F_u\] = The force of upthrust.
\( \delta P\) = Pressure difference between the top and bottom of the object.
\(A\) = Cross sectional area of the object perpendicular to the height.
Example Calculations
| A cube of 1m sides is submersed in water which has a density of 1000kg/m3 on Earth with a gravitational field strength of 9.8N/kg. | A cube of 20m sides is submersed in water which has a density of 1000kg/m3 on Earth with a gravitational field strength of 9.8N/kg. | A cube of 4m sides is submersed in water which has a density of 1000kg/m3 on Earth with a gravitational field strength of 9.8N/kg. |
Examples
| A boat floats on the water because the weight is balanced by the upthrust. | A submarine can change the amount of upthrust in order to rise or sink in the water. |