Difference between revisions of "Isotope"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
: Each [[element]] has many [[isotope]]s but some are [[Stable Isotope|stable]] and others are [[Unstable Isotope|unstable]] so they [[Radioactive Decay|decay]] quickly into other [[isotope]]s or a different [[element]]. | : Each [[element]] has many [[isotope]]s but some are [[Stable Isotope|stable]] and others are [[Unstable Isotope|unstable]] so they [[Radioactive Decay|decay]] quickly into other [[isotope]]s or a different [[element]]. | ||
: Different [[isotope]]s of the same [[element]] have the same [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] but different [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] due to the different numbers of [[neutron]]s. | : Different [[isotope]]s of the same [[element]] have the same [[Atomic Number|atomic number]] but different [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] due to the different numbers of [[neutron]]s. | ||
| + | : Different [[isotope]]s of the same [[element]] have the same [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]] but they have different [[Physical Property|physical properties]]. This means they cannot be separated by chemical processes but they can be separated by physical ones. | ||
| + | : Different [[isotope]]s of the same [[element]] may have different [[Boiling Point|boiling points]], different [[Melting Point|melting point]]s, may [[Diffusion|diffuse]] at different rates and, as has already been stated, have a different [[Relative Atomic Mass|mass]]. This means [[isotope]]s can be separated by processes such as [[Distillation]], [[Chromatography]] and [[Centrifuge]]. | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 32: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | === | + | ===Isotopic Abundance=== |
| + | : Different [[isotope]]s of the same [[element]] do not all appear in the same quantities. Some [[isotope]]s are more common than others. | ||
| + | : The [[Periodic Table]] orders the [[element]]s due to their [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]] but since [[isotope]]s of the same [[element]] have the same [[Chemical Property|chemical properties]] different [[isotope]]s are not included. Instead an [[average]] [[Relative Atomic Mass|atomic mass]] is given based on the [[Relative Atomic Mass|mass]] of each [[isotope]] and how common it is. | ||
Revision as of 12:03, 26 November 2018
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons (the same element) but a different number of neutrons.
About Isotopes
- Each element has many isotopes but some are stable and others are unstable so they decay quickly into other isotopes or a different element.
- Different isotopes of the same element have the same atomic number but different atomic mass due to the different numbers of neutrons.
- Different isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties but they have different physical properties. This means they cannot be separated by chemical processes but they can be separated by physical ones.
- Different isotopes of the same element may have different boiling points, different melting points, may diffuse at different rates and, as has already been stated, have a different mass. This means isotopes can be separated by processes such as Distillation, Chromatography and Centrifuge.
Examples
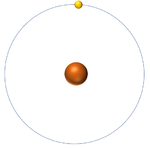
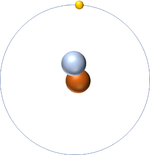
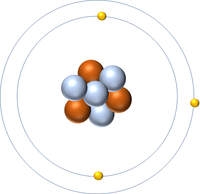
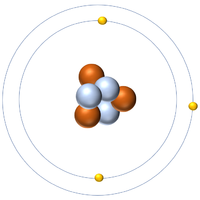
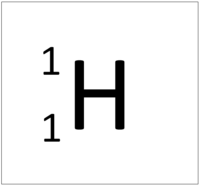
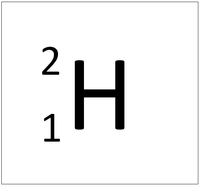
| Hydrogen-1 | Hydrogen-2 | Lithium-7 | Lithium-6 |
| Hydrogen always has 1 proton but isotope there are no neutrons. | Hydrogen always has 1 proton but in this isotope there is 1 neutron. This isotope of Hydrogen is known as Deuterium. | Lithium always has 3 protons but in this isotope there are 4 neutrons. | Lithium always has 3 protons but in this isotope there are 3 neutrons. |
Isotopic Abundance
- Different isotopes of the same element do not all appear in the same quantities. Some isotopes are more common than others.
- The Periodic Table orders the elements due to their chemical properties but since isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties different isotopes are not included. Instead an average atomic mass is given based on the mass of each isotope and how common it is.