Difference between revisions of "Mitosis"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
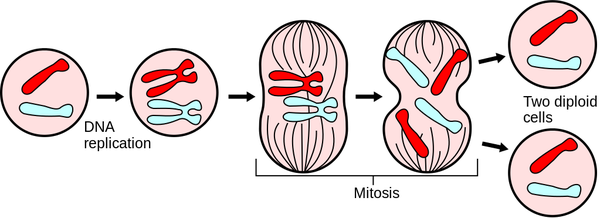
: During [[mitosis]] the [[Cell Nucleus|nucleus]] divides into two separate [[Cell Nucleus|nuclei]]. | : During [[mitosis]] the [[Cell Nucleus|nucleus]] divides into two separate [[Cell Nucleus|nuclei]]. | ||
: The two daughter [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] are called [[diploid]] [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] because they contain [[chromosome]]s in matching pairs. | : The two daughter [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] are called [[diploid]] [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] because they contain [[chromosome]]s in matching pairs. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:Mitosis.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the [[chromosome]]s during the process of [[mitosis]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 10:24, 5 November 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Cell Division is when a cell splits into two smaller, identical, cells.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Mitosis is the process of asexual reproduction where a parent cell splits into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent.
About Mitosis
- Mitosis is how unicellular organisms reproduce.
- Multicellular organisms grow by cells performing mitosis.
- The 2 daughter cells are genetically identical to each other.
- Before mitosis the cell spends its time copying the chromosomes.
- During mitosis the nucleus divides into two separate nuclei.
- The two daughter cells are called diploid cells because they contain chromosomes in matching pairs.
| A diagram showing the chromosomes during the process of mitosis. |