Difference between revisions of "Geothermal"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|[[File:GeothermalPowerStationDiagram.png|center|600px]] | |[[File:GeothermalPowerStationDiagram.png|center|600px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[geothermal]] [[power station]]. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of a [[geothermal]] [[Thermal Power Station|power station]]. |
|} | |} | ||
: 1. Cold water is pumped deep underground. | : 1. Cold water is pumped deep underground. | ||
Revision as of 08:21, 6 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Geothermal is an energy resource that allows us to use the thermal energy underground in volcanic regions to heat or to power electrical appliances.
About Geothermal
- Geothermal is a renewable energy resource.
- Geothermal has energy in the thermal energy store of rocks underneath the Earth's surface.
Power
Geothermal can be used to provide hot water or generate electricity.
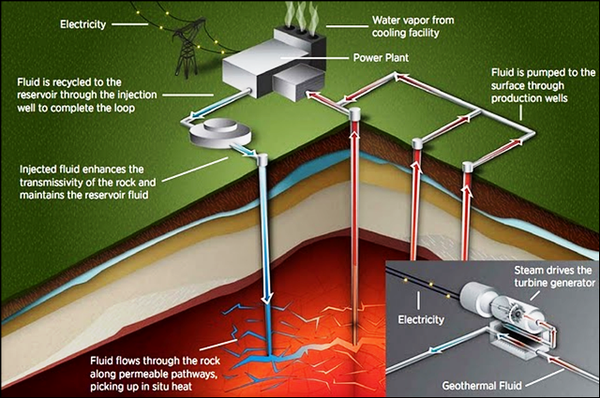
| A diagram of a geothermal power station. |
- 1. Cold water is pumped deep underground.
- 2. Water is heated as it passes through rocks underground.
- 3. Water turns to steam and passes down pipes to turn a turbine.
- 4. The turbine causes a generator to spin.
- 5. The generator makes an electrical current.
Advantages
- Extremely reliable (does not depend on sunlight or wind).
- Can be used to generate electrical power or to heat buildings directly.
- Does not cause pollution or significant environmental damage.
- No fuel cost.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to build when compared to how much money can be made selling the power.
- Can only be built in volcanic areas.