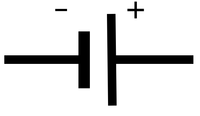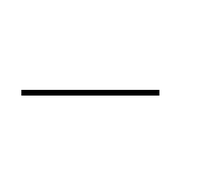Difference between revisions of "Electrical Component"
(→About Components) |
|||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
*[[Ammeter]] | *[[Ammeter]] | ||
| − | + | ===Examples=== | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
|'''Wires''' | |'''Wires''' | ||
|'''Filament Bulb''' | |'''Filament Bulb''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:CellSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:WireSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:BulbSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:ElectricalCell.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:ElectricalCell.png|center|200px]] | ||
| Line 82: | Line 86: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Wires are the path for electricity to flow. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Wires are the path for electricity to flow. | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A filament bulb lights up when electricity flows through it. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A filament bulb lights up when electricity flows through it. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Switch''' | |'''Switch''' | ||
|'''Buzzer''' | |'''Buzzer''' | ||
|'''Motor''' | |'''Motor''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:SwitchOpenSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:BuzzerSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:MotorSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:ElectricalSwitch.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:ElectricalSwitch.png|center|200px]] | ||
| Line 94: | Line 104: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A buzzer makes a sound when electricity flows through it. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A buzzer makes a sound when electricity flows through it. | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A motor spins when electricity flows through it. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A motor spins when electricity flows through it. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Resistor''' | |'''Resistor''' | ||
| − | |''' | + | |'''Voltmeter''' |
| − | |''' | + | |'''Ammeter''' |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ResistorSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:VoltmeterSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:AmmeterSymbol.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Resistor.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:Resistor.png|center|200px]] | ||
Revision as of 11:55, 31 October 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A component is a part of an electrical circuit.
About Components
- Components in a circuit are used to do different jobs.
- The components you should know are:
Examples
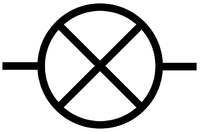
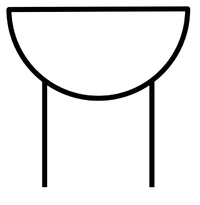
| Electrical Cell | Wires | Filament Bulb |
| A cell makes the electricity flow in a circuit. | Wires are the path for electricity to flow. | A filament bulb lights up when electricity flows through it. |
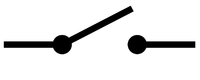
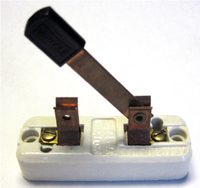
| Switch | Buzzer | Motor |
| A switch can complete or break a circuit to turn it on and off. | A buzzer makes a sound when electricity flows through it. | A motor spins when electricity flows through it. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A component is a part of an electrical circuit.
About Components
- Components in a circuit are used to do different jobs.
- The components you should know are:
Examples
| Electrical Cell | Wires | Filament Bulb |
| A cell makes the electricity flow in a circuit. | Wires are the path for electricity to flow. | A filament bulb lights up when electricity flows through it. |
| Switch | Buzzer | Motor |
| A switch can complete or break a circuit to turn it on and off. | A buzzer makes a sound when electricity flows through it. | A motor spins when electricity flows through it. |
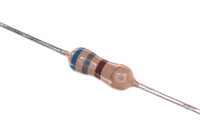
| Resistor | Voltmeter | Ammeter |
| A resistor reduces the flow of current through a circuit. | A Voltmeter is used to measure the Potential Difference between two points on a circuit. | An Ammeter is used to measure the Current passing through part of a circuit. |