Difference between revisions of "Circuit"
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
A '''circuit''' is a loop of [[wire]] that [[electricity]] flows around. | A '''circuit''' is a loop of [[wire]] that [[electricity]] flows around. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Circuits=== | ||
| + | : [[Circuit]]s can have [[component]]s in [[Series Circuit|series]] or [[Parallel Circuit|parallel]]. | ||
| + | : [[Component]]s in [[Parallel Circuit|parallel]] in a [[circuit]] have the same [[Potential Difference]] across them but share the [[Electrical Current|Current]]. | ||
| + | : [[Component]]s in [[Series Circuit|series]] in a [[circuit]] have the same [[Electrical Current|Current]] through them but share the [[Potential Difference]]. | ||
===Energy Transfers=== | ===Energy Transfers=== | ||
Revision as of 11:27, 31 October 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A circuit is a loop of wire that electricity flows around.
About Circuits
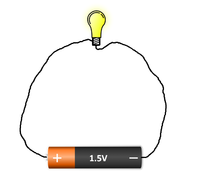
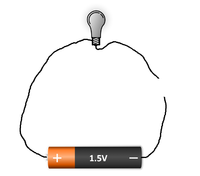
- A circuit needs to be complete otherwise electricity will not flow through it. Any break in the circuit will stop the electricity from flowing.
- A circuit starts and ends at the source of power. This is usually a battery or cell but it can be a generator or Solar Cell.
| A circuit must be a complete loop without any breaks or it will not work. | The break in this circuit stops it from working. |
To practice building a circuit you can use a circuit simulator by clicking on the picture below.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A circuit is a loop of wire that electricity flows around.
About Circuits
- Circuits can have components in series or parallel.
- Components in parallel in a circuit have the same Potential Difference across them but share the Current.
- Components in series in a circuit have the same Current through them but share the Potential Difference.
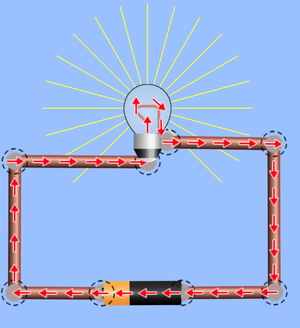
Energy Transfers
Cell
- Energy is transferred electrically out of the chemical potential energy store.
Light Bulb
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the thermal energy store of the bulb.
- Energy is also transferred away from the bulb by light radiation.
Motor
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the kinetic energy store of the motor as it speeds up.
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the thermal energy store of the motor due to friction.
Speaker or Buzzer
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the kinetic energy store of the Speaker.
- Energy is also transferred away from the Speaker by sound radiation.