Difference between revisions of "Wave"
(→Examples) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File:WaterWave. | + | |[[File:WaterWave.gif|center]] |
|[[File:Picture.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:Picture.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 16 October 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
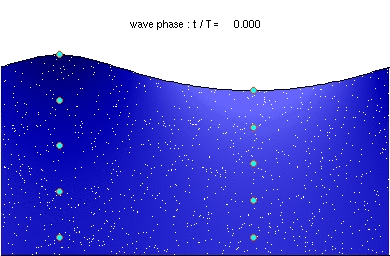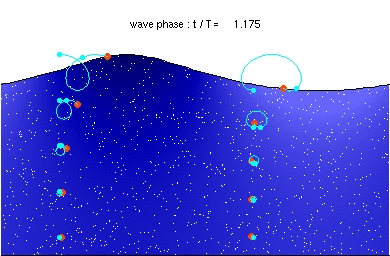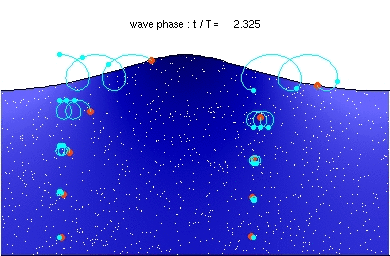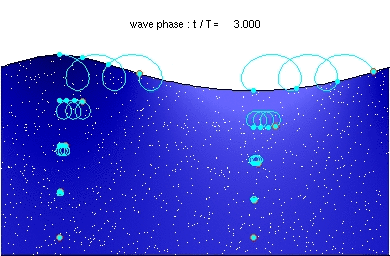
A wave is a vibration that transfers energy from one location to another.
About Waves
- Waves can transmit energy and information from one place to another.
- Waves travel through a medium that allows the vibration.
- There are two types of wave; transverse and longitudinal.
- In longitudinal waves the vibration is in the same direction as the energy transfer.
- In transverse waves the vibration is perpendicular to the direction as the energy transfer.
Examples
| Transverse Wave | Longitudinal Wave |
| This is a transverse wave on a string where the vibration is perpendicular to the motion of the wave. | This is a longitudinal wave on a string where the vibration is parallel to the motion of the wave. |
| Text | Text |
| Text | Text |