Difference between revisions of "Evaporation of Solutions"
(→About Evaporation of Solutions) |
(→Meaning) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | '''Evaporation of a solution''' is a way to recover the [[solute]] that has been [[dissolve]]d in a [[solvent]]. | + | '''Evaporation of a solution''' is a way to [[Separating Mixtures|separate]] the [[mixture]] of a [[solution]] to recover the [[solute]] that has been [[dissolve]]d in a [[solvent]]. |
===About Evaporation of Solutions=== | ===About Evaporation of Solutions=== | ||
Revision as of 12:07, 27 September 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Evaporation of a solution is a way to get back a solid that has been dissolved in a liquid.
About Evaporation of Solutions
| You can separate salt from the water by evaporating the water in an evaporating dish. |
Examples
| These people collect salt by putting sea water in small ponds and allowing the warm temperatures to evaporate the water away leaving the behind the salt. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Evaporation of a solution is a way to separate the mixture of a solution to recover the solute that has been dissolved in a solvent.
About Evaporation of Solutions
- The evaporation of solutions recovers the solutes but loses the solvent.
- Evaporation of solutions can be done by directly heating the solution or by giving time for the liquid to evaporate at low temperatures.
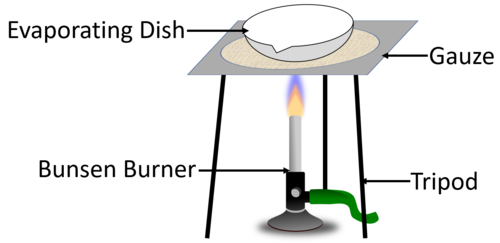
| The diagram shows the experimental setup to evaporate away the solvent to leave behind the solute in the evaporating dish. |