Difference between revisions of "Amplitude"
(→Meaning) |
(→Key Stage 5) |
||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
*Measures the strength or [[intensity]] of a [[wave]]. | *Measures the strength or [[intensity]] of a [[wave]]. | ||
*Larger [[amplitude]] means more [[energy]] is carried by the wave. | *Larger [[amplitude]] means more [[energy]] is carried by the wave. | ||
| − | *Can be [[measure]]d in various units depending on the type of [[wave]] (e.g., | + | *Can be [[measure]]d in various units depending on the type of [[wave]] (e.g., [[metres]] for [[Mechanical Wave|mechanical waves]], [[volt]]s for electrical signals). |
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
*The loudness of a [[sound]] is related to the [[amplitude]] of the [[sound]] wave. | *The loudness of a [[sound]] is related to the [[amplitude]] of the [[sound]] wave. | ||
*The brightness of a [[Visible Light|light]] [[wave]] increases with its [[amplitude]]. | *The brightness of a [[Visible Light|light]] [[wave]] increases with its [[amplitude]]. | ||
Revision as of 09:04, 19 May 2024
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
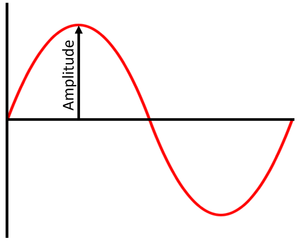
The amplitude of a wave is the distance between the peak of a wave and the midpoint of the wave.
About Amplitude
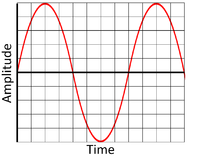
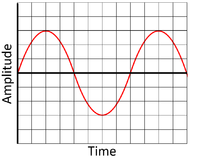
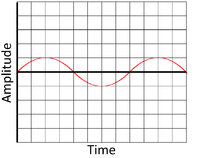
The greater the amplitude of:
| This is a high amplitude wave. | This is a low amplitude wave. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement of the wave from its equilibrium position.
About Amplitude
The greater the amplitude of:
| This is a high amplitude wave shown by the large displacement between the peak (or trough) of the wave and the equilibrium position. | This is a low amplitude wave shown by the small displacement between the peak (or trough) of the wave and the equilibrium position. |
References
AQA
- Amplitude (A), page 183, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA'
- Amplitude (waves), page 219, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'
- Amplitude, page 189, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA'
- Amplitude, page 226, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA'
- Amplitude, page 73, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'
- Amplitude, pages 176, 182, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA'
- Amplitude, pages 191-2, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA'
- Amplitude, pages 257, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA'
Edexcel
- Amplitude, page 164, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Amplitude, page 32, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Amplitude, page 331, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Amplitude, page 49, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Amplitude, page 91, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
- Amplitude (waves), pages 142-143, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Amplitude, page 186, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Amplitude, page 59, Gateway GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
Key Stage 5
Meaning
Amplitude is the maximum displacement from equilibrium in an oscillating system.
About Amplitude
- Measures the strength or intensity of a wave.
- Larger amplitude means more energy is carried by the wave.
- Can be measured in various units depending on the type of wave (e.g., metres for mechanical waves, volts for electrical signals).