Difference between revisions of "Microphone"
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Microphones, page 307, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Microphones, page 307, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac312 ''Microphones, page 97, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac312 ''Microphones, page 97, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Microphones, page 175, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Microphones, page 284, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Microphones, page 90, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 22 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning

A picture of a microphone.
A microphone is an electrical device that turns the vibration of a sound into an electrical signal.
About Microphones
- Sound transfers information which a microphone converts into an electrical signal.
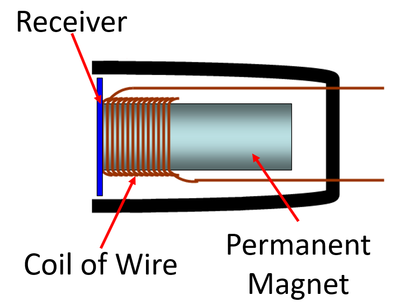
- Microphones use a coil of wire and a permanent magnet to turn a vibration into an electrical signal.
- When the receiver vibrates the coil of wire moves around the permanent magnet to make a current in the coil of wire.
| A diagram of a microphone. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning

A picture of a microphone.
A microphone is an electrical device that turns the vibration of a sound into an electrical signal using the generator effect.
About Microphones
- Sound transfers information which a microphone converts into an electrical signal.
- Microphones use a coil of wire and a permanent magnet to induce a current in the coil when receiver vibrates.
- When the receiver vibrates the coil of wire moves around the permanent magnet to make a current in the coil of wire.
| A diagram of a microphone. |
References
AQA
- Microphone, moving-coil, pages 195, 262, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Microphones, page 225, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Microphones, page 235, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Microphones, page 307, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Microphones, page 97, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA