Difference between revisions of "Strong Nuclear Interaction"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===About The Strong Nuclear Interaction=== | ===About The Strong Nuclear Interaction=== | ||
: The '''strong nuclear interaction''' is one of the 4 [[Fundamental Interactions|fundamental interactions]] governing how [[Subatomic Particle|subatomic particles]] affect one another. | : The '''strong nuclear interaction''' is one of the 4 [[Fundamental Interactions|fundamental interactions]] governing how [[Subatomic Particle|subatomic particles]] affect one another. | ||
| + | : [[Lepton]]s are unaffected by the '''strong nuclear interaction'''. | ||
: The '''strong nuclear interaction''' holds [[quark]]s together within [[baryon]]s. | : The '''strong nuclear interaction''' holds [[quark]]s together within [[baryon]]s. | ||
: The '''strong nuclear interaction''' holds [[proton]]s and [[neutron]]s together in the [[Atomic Nucleus|atomic nucleus]]. | : The '''strong nuclear interaction''' holds [[proton]]s and [[neutron]]s together in the [[Atomic Nucleus|atomic nucleus]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:18, 18 July 2019
Key Stage 5
Meaning
The strong nuclear interaction is mechanism governing how hadrons affect one another.
About The Strong Nuclear Interaction
- The strong nuclear interaction is one of the 4 fundamental interactions governing how subatomic particles affect one another.
- Leptons are unaffected by the strong nuclear interaction.
- The strong nuclear interaction holds quarks together within baryons.
- The strong nuclear interaction holds protons and neutrons together in the atomic nucleus.
- The strong nuclear interaction is mediated by gluons.
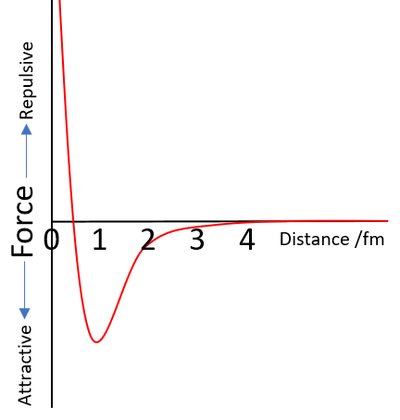
| The strong nuclear interaction is attractive at a range of 0.5fm to around 3-4fm and is repulsive below 0.5fm. |