Difference between revisions of "Mitochondria"
(→Examples) |
(→About Mitochondria) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
===About Mitochondria=== | ===About Mitochondria=== | ||
| − | : [[Mitochondria]] are used to release the energy from food. | + | : [[Mitochondria]] are used to release the [[energy]] from food. |
: [[Cell (Biology)|Cells]] that need more energy have more [[mitochondria]]. | : [[Cell (Biology)|Cells]] that need more energy have more [[mitochondria]]. | ||
: [[Sperm Cell|Sperm cells]] have a lot of [[mitochondria]] to provide the energy needed to swim to the [[Ovum|egg cell]]. | : [[Sperm Cell|Sperm cells]] have a lot of [[mitochondria]] to provide the energy needed to swim to the [[Ovum|egg cell]]. | ||
Revision as of 19:42, 4 June 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
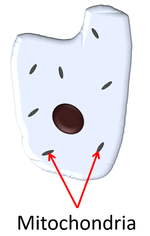
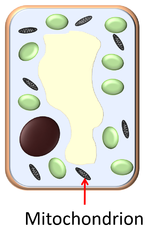
A Mitochondrion is a part of a cell where respiration takes place.
Function
Mitochondria provide energy to the cell by respiration.
About Mitochondria
- Mitochondria are used to release the energy from food.
- Cells that need more energy have more mitochondria.
- Sperm cells have a lot of mitochondria to provide the energy needed to swim to the egg cell.
- Mitochondria are found in plant cells, animal cells and fungal cells but are not found in Bacteria.
Examples
| Animal Cell | Sperm Cell | Root Hair Cell | Palisade Cell |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A mitochondrion is membrane bound organelle found in eukarytotic cells that is the site of respiration.
Function
- Mitochondria provide energy to the cell by aerobic respiration of glucose.
About Mitochondria
- Mitochondria have their own DNA inside them and are roughly the size of a bacterium which suggests they were once an independent organism that migrated into eukaryotic cells.