Difference between revisions of "Circuit"
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
: [[Energy]] is [[Energy Transfer|transferred]] [[Electrical Energy Transfer|electrically]] into the the [[Kinetic Energy Store|kinetic energy store]] of the [[Speaker]]. | : [[Energy]] is [[Energy Transfer|transferred]] [[Electrical Energy Transfer|electrically]] into the the [[Kinetic Energy Store|kinetic energy store]] of the [[Speaker]]. | ||
: [[Energy]] is also [[Energy Transfer|transferred]] away from the [[Speaker]] by [[sound]] [[radiation]]. | : [[Energy]] is also [[Energy Transfer|transferred]] away from the [[Speaker]] by [[sound]] [[radiation]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09776 ''Circuits, pages 180, 185, 186, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac50 ''Circuits, pages 24-33, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09781 ''Circuits, series, page 185, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Circuits; circuit diagrams, pages 60, 61, 235, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Circuits; circuit diagrams, pages 62, 63, 331, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09777 ''Circuits; investigating I-V characteristics, page 183, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09778 ''Circuits; investigating resistance, pages 182, 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Circuits; parallel circuits, pages 72-76, 78, 79, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Circuits; parallel circuits, pages 74-78, 80, 81, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09779 ''Circuits; parallel, page 186, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Circuits; parallel, page 302, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09780 ''Circuits; sensing, page 184, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Circuits; sensor circuits, page 81, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Circuits; sensor circuits, page 83, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Circuits; series circuits, pages 68-71, 77, 78, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Circuits; series circuits, pages 70-73, 79, 80, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Circuits; series, pages 295, 301-2, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Circuits; standard test circuit, page 67, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 11:59, 3 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A circuit is a loop of wire that electricity flows around.
About Circuits
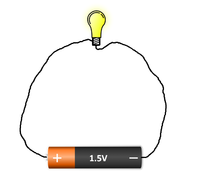
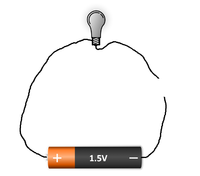
- A circuit needs to be complete otherwise electricity will not flow through it. Any break in the circuit will stop the electricity from flowing.
- A circuit starts and ends at the source of power. This is usually a battery or cell but it can be a generator or Solar Cell.
| A circuit must be a complete loop without any breaks or it will not work. | The break in this circuit stops it from working. |
To practice building a circuit you can use a circuit simulator by clicking on the picture below.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A circuit is a loop of wire that electricity flows around.
About Circuits
- Circuits can have components in series or parallel.
- Components in parallel in a circuit have the same Potential Difference across them but share the Current.
- Components in series in a circuit have the same Current through them but share the Potential Difference.
Examples
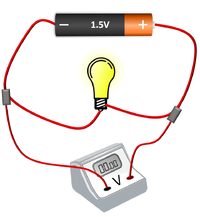
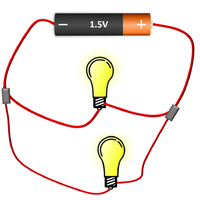
| The bulb and Ammeter are in series so they have the same Current going through them. | The cell, bulb and Voltmeter are in parallel so they have the same Potential Difference across them. | The two bulbs are in parallel so they have the same Potential Difference across them but may have a different Current passing through them. |
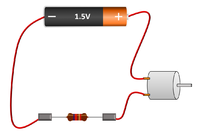
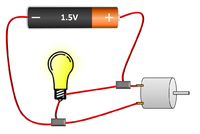
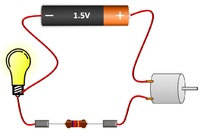
| The motor and resistor are in series so they have the same Current passing through them but share the 1.5V Potential Difference between them. | The bulb and motor are in parallel so they have the same Potential Difference across them but may have a different Current passing through them. | The motor, resistor and bulb are in series so they all have the same Current passing through them but share the 1.5V Potential Difference between them. |
Energy Transfers
Cell
- Energy is transferred electrically out of the chemical potential energy store.
Light Bulb
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the thermal energy store of the bulb.
- Energy is also transferred away from the bulb by light radiation.
Motor
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the kinetic energy store of the motor as it speeds up.
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the thermal energy store of the motor due to friction.
Speaker or Buzzer
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the kinetic energy store of the Speaker.
- Energy is also transferred away from the Speaker by sound radiation.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A circuit is a loop of wire that electricity flows around.
About Circuits
- Circuits can have components in series or parallel.
- Components in parallel in a circuit have the same Potential Difference across them but share the current.
- Components in series in a circuit have the same Current through them but share the potential difference.
Examples
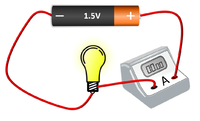
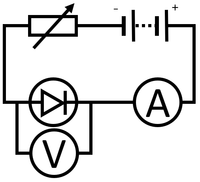
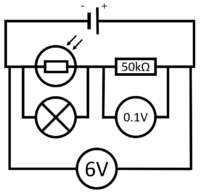
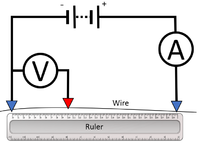
| This circuit can be used to plot the IV Graph for a diode. | This circuit can be used to activate a lamp when it is dark. | This circuit can be used to find the resistance of a wire. |
Energy Transfers
Cell
- Energy is transferred electrically out of the chemical potential energy store.
Light Bulb
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the thermal energy store of the bulb.
- Energy is also transferred away from the bulb by light radiation.
Motor
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the kinetic energy store of the motor as it speeds up.
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the thermal energy store of the motor due to friction.
Electrical Heater
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the thermal energy store of the heater.
Speaker or Buzzer
- Energy is transferred electrically into the the kinetic energy store of the Speaker.
- Energy is also transferred away from the Speaker by sound radiation.
References
AQA
- Circuits, pages 180, 185, 186, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Circuits, pages 24-33, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Circuits, series, page 185, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; circuit diagrams, pages 60, 61, 235, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; circuit diagrams, pages 62, 63, 331, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; investigating I-V characteristics, page 183, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; investigating resistance, pages 182, 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; parallel circuits, pages 72-76, 78, 79, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; parallel circuits, pages 74-78, 80, 81, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; parallel, page 186, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; parallel, page 302, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Circuits; sensing, page 184, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; sensor circuits, page 81, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; sensor circuits, page 83, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; series circuits, pages 68-71, 77, 78, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; series circuits, pages 70-73, 79, 80, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Circuits; series, pages 295, 301-2, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Circuits; standard test circuit, page 67, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA