Difference between revisions of "Uncertainty"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== Uncertainty is the amount by which a reading may be different from the true value. ===About Uncertainty=== : Uncertainty is caused b...") |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:ResultsTableCalculation.png|center|400px]] | |[[File:ResultsTableCalculation.png|center|400px]] | ||
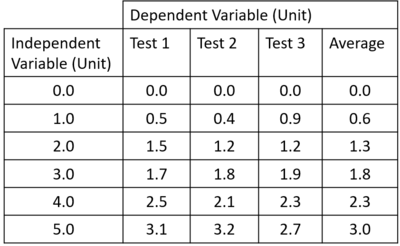
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[range]] is found by | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[range]] is found by subtracting the smallest from the largest value and the [[uncertainty]] can be found by halving that [[range]]. |
The [[uncertainty|uncertainties]] in this [[Table of Results|results table]] are: | The [[uncertainty|uncertainties]] in this [[Table of Results|results table]] are: | ||
Revision as of 13:02, 6 April 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Uncertainty is the amount by which a reading may be different from the true value.
About Uncertainty
- Uncertainty is caused by random errors which take place during an experiment.
- The uncertainty in a reading can be found by repeating the reading and halving the range of those readings.
\(Uncertainty=\frac{range}{2}\).
- The uncertainty in a result is how far above or below the average result the true value may be.
Examples
| The range is found by subtracting the smallest from the largest value and the uncertainty can be found by halving that range.
The uncertainties in this results table are: 0/2 = 0 0.5/2 = 0.25 0.3/2 = 0.15 0.2/2 = 0.1 0.4/2 = 0.2 0.5/2 = 0.25 |