Difference between revisions of "Alpha Particle"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | An '''alpha particle''' is a type of [[Ionising Radiation|ionising radiation]] made of 2 [[proton]]s and 2 [[neutron]]s [[emit]]ted from the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] of an [[Unstable Isotope|unstable isotope]]. | + | An '''alpha particle''' ('''α-particle''') is a type of [[Ionising Radiation|ionising radiation]] made of 2 [[proton]]s and 2 [[neutron]]s [[emit]]ted from the [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] of an [[Unstable Isotope|unstable isotope]]. |
===About Alpha Particles=== | ===About Alpha Particles=== | ||
| − | : '''Alpha particles''' may also be referred to as '''alpha radiation'''. | + | : '''Alpha particles''' may also be referred to as '''alpha radiation''' and is written with the symbol '''α'''. |
: '''Alpha particles''' are a [[Helium]] [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | : '''Alpha particles''' are a [[Helium]] [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]]. | ||
: '''Alpha particles''' have a [[Relative Atomic Mass|relative atomic mass]] of 4 and [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative charge]] of +2. | : '''Alpha particles''' have a [[Relative Atomic Mass|relative atomic mass]] of 4 and [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative charge]] of +2. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
: '''Alpha particles''' are [[emit]]ted rather than single [[proton]]s or [[neutron]]s because the [[Helium]] [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is extremely [[Stable Isotope|stable]]. | : '''Alpha particles''' are [[emit]]ted rather than single [[proton]]s or [[neutron]]s because the [[Helium]] [[Atomic Nucleus|nucleus]] is extremely [[Stable Isotope|stable]]. | ||
| + | ====Charge and Mass==== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:AlphaParticleCharge.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:AlphaParticleCharge.png|center|200px]] | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:left;" |Scientist were able to determine the [[Electrical Charge|charge]] and [[mass]] of [[Alpha Particle| | + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:left;" |Scientist were able to determine the [[Electrical Charge|charge]] and [[mass]] of [[Alpha Particle|α-particle]] by sending it between two [[Electrical Charge|electrically charged]] plates and observing its path. |
| − | The ''' | + | The '''α-particle''' moves towards the [[Negative Charge|negative]] plate, so it must be [[Positive Charge|positively charged]]. The rate of curvature depends on the [[mass]]:[[Electrical Charge|charge]] [[ratio]] which indicates it has a [[Relative Atomic Mass|relative atomic mass]] of 4 and [[Relative Atomic Charge|relative charge]] of +2. |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Penetration Depth==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:AlphaPenetrationAir.png|center|200px]] | ||
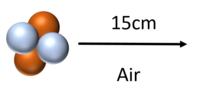
| + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:left;" |[[Alpha Particle|Alpha particles]] can travel around 5cm through [[air]] ([[STP]]) before [[colliding]] with and [[ionising]] [[atom]]s or [[molecule]]s. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:AlphaPenetration.png|center|200px]] | ||
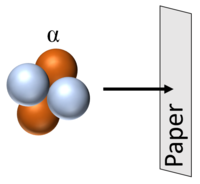
| + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:left;" |[[Alpha Particle|Alpha particles]] can be stopped by a thin sheet of paper. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Ionising Potential=== | ||
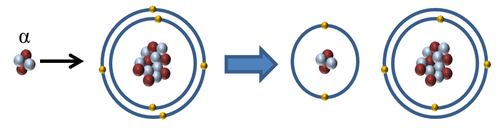
| + | : With a [[Electrical Charge|charge]] of +2, '''α-particles''' are the most [[Ionising Radiation|ionising]] of the three [[Ionising Radiation|ionising radiations]]. It is capable of removing two [[electron]]s from a single [[atom]] or [[molecule]] or removing 1 [[electron]] from two [[atom]]s or [[molecule]]s. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:AlphaIonise.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" |When an [[Alpha Particle|α-particle]] interacts with an [[atom]] the [[Alpha Particle|α-particle]] can remove one or two [[electron]]s to '''ionise''' the [[atom]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Precautions=== | ||
| + | : [[Alpha Particle|Alpha radiation]] is the most [[Ionising Radiation|ionising]] but the least [[Penetration Depth|penetrating]]. | ||
| + | : Outside the body an [[organism]] can be protected from [[Alpha Particle|alpha radiation]] by keeping a distance greater than 5cm or by covering any bare skin. | ||
| + | : When handling a source of [[Alpha Particle|alpha radiation]] the precautions which should be taken are: | ||
| + | :*Wear gloves | ||
| + | :*Use tongs to handle the source, never touch it. | ||
| + | :*Aim the source away from any living [[organism]]. | ||
| + | :*Store the source in a sealed container. | ||
Revision as of 16:43, 7 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An alpha particle (α-particle) is a type of ionising radiation made of 2 protons and 2 neutrons emitted from the nucleus of an unstable isotope.
About Alpha Particles
- Alpha particles may also be referred to as alpha radiation and is written with the symbol α.
- Alpha particles are a Helium nucleus.
- Alpha particles have a relative atomic mass of 4 and relative charge of +2.
- Alpha particles are emitted when a nucleus is too large or the ratio of protons to neutrons is too large.
- Alpha particles are emitted rather than single protons or neutrons because the Helium nucleus is extremely stable.
Charge and Mass
| Scientist were able to determine the charge and mass of α-particle by sending it between two electrically charged plates and observing its path.
The α-particle moves towards the negative plate, so it must be positively charged. The rate of curvature depends on the mass:charge ratio which indicates it has a relative atomic mass of 4 and relative charge of +2. |
Penetration Depth
| Alpha particles can travel around 5cm through air (STP) before colliding with and ionising atoms or molecules. |
| Alpha particles can be stopped by a thin sheet of paper. |
Ionising Potential
- With a charge of +2, α-particles are the most ionising of the three ionising radiations. It is capable of removing two electrons from a single atom or molecule or removing 1 electron from two atoms or molecules.
| When an α-particle interacts with an atom the α-particle can remove one or two electrons to ionise the atom. |
Precautions
- Alpha radiation is the most ionising but the least penetrating.
- Outside the body an organism can be protected from alpha radiation by keeping a distance greater than 5cm or by covering any bare skin.
- When handling a source of alpha radiation the precautions which should be taken are:
- Wear gloves
- Use tongs to handle the source, never touch it.
- Aim the source away from any living organism.
- Store the source in a sealed container.