Difference between revisions of "Magnet"
(→About Magnets) |
(→Key Stage 3) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
A '''magnet''' is an object that [[attract]]s [[Iron]], [[Cobalt]] or [[Nickel]]. | A '''magnet''' is an object that [[attract]]s [[Iron]], [[Cobalt]] or [[Nickel]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Magnets=== | ||
| + | : There are three types of [[magnet]] you should know: | ||
| + | *[[Permanent Magnet]]s - These are [[magnet]]s which have a permanent [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] which needs [[energy]] to be removed. | ||
| + | *[[Induced Magnet]]s - These are [[Magnetic Material|magnetic materials]] which only become [[magnet]]s when they are in the [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] of another [[magnet]]. | ||
| + | *[[Electromagnet]]s - These are a coil of wire wrapped around a [[Soft Iron|soft iron]] core. They only become [[magnet]]s when there is a [[Electrical Current|current]] passed through the coil of wire. | ||
| + | : '''Magnets''' are [[attract]]ed to some [[metal]]s ([[Cobalt]], [[Nickel]] and [[Iron]]). Those [[metal]]s are '''magnetic''' but they are not [[magnet]]s themselves. | ||
| + | : '''Magnets''' have two [[poles]]; North and South. | ||
| + | : When two North [[Poles]] are placed next to each other two '''magnets''' will [[repel]] each other. | ||
| + | : When two South [[Poles]] are placed next to each other two '''magnets''' will [[repel]] each other. | ||
| + | : When the North [[Poles|Pole]] of one '''magnet''' is placed next to the South [[Poles|Pole]] of another '''magnet''' they [[attract]] each other. | ||
| + | : All [[magnet]]s have a [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] around them which influences other [[Magnetic Material|magnetic materials]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:MagneticFieldLines.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:MagneticFieldLinesElectromagnet.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
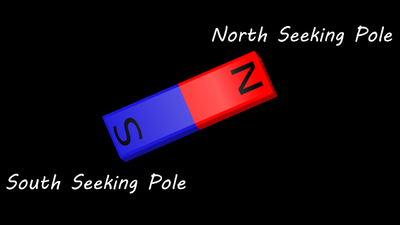
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Bar Magnet|bar magnet]] is a [[Permanent Magnet|permanent magnet]]. | ||
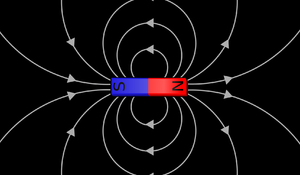
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This is a [[diagram]] of an [[electromagnet]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | A '''magnet''' is an [[object]] that produces its own [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]. | ||
===About Magnets=== | ===About Magnets=== | ||
Revision as of 08:46, 4 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 1
Meaning
A magnet is an object that sticks to some metals.
About Magnets
- Magnets are very useful. We can use them to stick notes to the fridge.
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A magnet is a piece of equipment that can be used to do determine if a material is magnetic.
About Magnets
- Magnets are attracted to some metals. Those metals are magnetic but they are not magnets themselves.
- Magnets have two poles; North and South.
- When two North Poles are placed next to each other two magnets will repel each other.
- When two South Poles are placed next to each other two magnets will repel each other.
- When the North Pole of one magnet is placed next to the South Pole of another magnet they attract each other.
Examples
| Magnets are attracted to some metals. Those metals are magnetic but they are not magnets themselves. | Magnets have two poles; North and South. |
| Two magnets facing North-North will repel each other and two magnets facing South-South will repel each other. | Two magnets facing North-South will attract each other. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A magnet is an object that attracts Iron, Cobalt or Nickel.
About Magnets
- There are three types of magnet you should know:
- Permanent Magnets - These are magnets which have a permanent magnetic field which needs energy to be removed.
- Induced Magnets - These are magnetic materials which only become magnets when they are in the magnetic field of another magnet.
- Electromagnets - These are a coil of wire wrapped around a soft iron core. They only become magnets when there is a current passed through the coil of wire.
- Magnets are attracted to some metals (Cobalt, Nickel and Iron). Those metals are magnetic but they are not magnets themselves.
- Magnets have two poles; North and South.
- When two North Poles are placed next to each other two magnets will repel each other.
- When two South Poles are placed next to each other two magnets will repel each other.
- When the North Pole of one magnet is placed next to the South Pole of another magnet they attract each other.
- All magnets have a magnetic field around them which influences other magnetic materials.
Examples
| The bar magnet is a permanent magnet. | This is a diagram of an electromagnet. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A magnet is an object that produces its own magnetic field.
About Magnets
- There are three types of magnet you should know:
- Permanent Magnets - These are magnets which have a permanent magnetic field which needs energy to be removed.
- Induced Magnets - These are magnetic materials which only become magnets when they are in the magnetic field of another magnet.
- Electromagnets - These are a coil of wire wrapped around a soft iron core. They only become magnets when there is a current passed through the coil of wire.
- Magnets are attracted to some metals (Cobalt, Nickel and Iron). Those metals are magnetic but they are not magnets themselves.
- Magnets have two poles; North and South.
- When two North Poles are placed next to each other two magnets will repel each other.
- When two South Poles are placed next to each other two magnets will repel each other.
- When the North Pole of one magnet is placed next to the South Pole of another magnet they attract each other.
- All magnets have a magnetic field around them which influences other magnetic materials.
Examples
| The bar magnet is a permanent magnet. | This is a diagram of an electromagnet. |