Difference between revisions of "Light Dependent Resistor"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|[[File:LDRPotentialDivider1.png|center|300px]] | |[[File:LDRPotentialDivider1.png|center|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
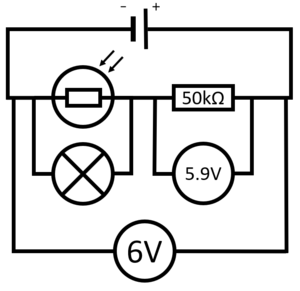
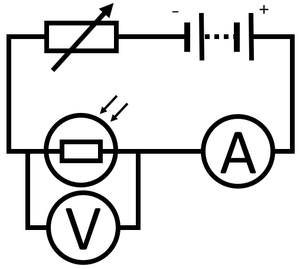
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |In this [[Circuit Diagram|circuit diagram]] the [[light]] intensity is low, which causes the [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] of the '''LDR''' to be high. As a result the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the [[electrical | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |In this [[Circuit Diagram|circuit diagram]] the [[light]] intensity is low, which causes the [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] of the '''LDR''' to be high. As a result the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the [[electrical Bulb|lamp]] will be high (5.9V) and the [[Electrical Current|current]] through the [[Electrical Bulb|lamp]] will be large. So in dim [[light]] the [[Electrical Bulb|lamp]] will remain lit. |
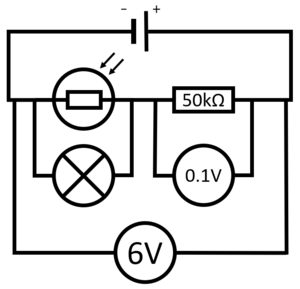
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |In this [[Circuit Diagram|circuit diagram]] the [[light]] intensity is high, which causes the [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] of the '''LDR''' to be low. As a [[result]] the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the [[electrical | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |In this [[Circuit Diagram|circuit diagram]] the [[light]] intensity is high, which causes the [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] of the '''LDR''' to be low. As a [[result]] the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the [[electrical Bulb|lamp]] will be low (0.1V) and the [[Electrical Current|current]] through the [[Electrical Bulb|lamp]] will be low. So in bright [[light]] the [[Electrical Bulb|lamp]] will remain unlit. |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 10:20, 8 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
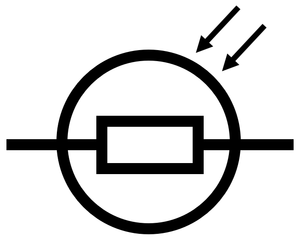
A light dependent resistor (LDR) is a resistor which changes resistance depending on the intensity of light that it is exposed to.
About Light Dependent Resistors
- Light dependent resistors decrease resistance as the intensity of light increases.
- A light dependent resistor can be used to control the current passing through a circuit. If the potential difference is constant then the current decreases as the light intensity decreases.
- A light dependent resistor can be used to control the potential difference of another component in series with it. If the light intensity on the light dependent resistor is decreased then the potential difference across other components will decrease.
- Light dependent resistors can be used in security lights and street lamps which activate depending on how dark it is.
IV Graph
| In this circuit diagram the light intensity is low, which causes the resistance of the LDR to be high. As a result the potential difference across the lamp will be high (5.9V) and the current through the lamp will be large. So in dim light the lamp will remain lit. | In this circuit diagram the light intensity is high, which causes the resistance of the LDR to be low. As a result the potential difference across the lamp will be low (0.1V) and the current through the lamp will be low. So in bright light the lamp will remain unlit. |
IV Graph
Description
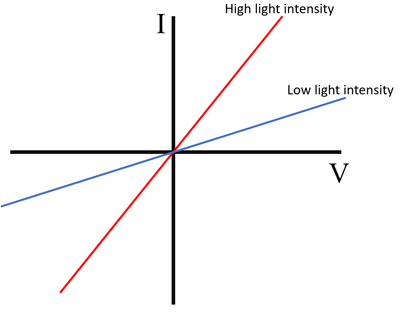
The IV Graph for a light dependent resistor shows that:
- At a high light intensity the current increases rapidly with the potential difference
- At a low light intensity the current increases slowly with the potential difference.
Explanation
- The resistance of an LDR increases as the light intensity decreases.
Obtaining the IV Graph
|