Difference between revisions of "Thermistor"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== right|300px|thumb|The symbol for a '''thermistor'''. A '''thermistor''' is a resistor which changes Electrica...") |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===About Thermistors=== | ===About Thermistors=== | ||
| − | : 'NTC' '''thermistors''' decrease [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] as the [[temperature]] increases. | + | : 'NTC' '''thermistors''' decrease [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] as the [[temperature]] increases. (NTC = Negative Temperature Coefficient.) |
: A '''thermistor''' can be used to control the [[Electrical Current|current]] passing through a [[circuit]]. If the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] is constant then the [[Electrical Current|current]] decreases as [[temperature]] decreases. | : A '''thermistor''' can be used to control the [[Electrical Current|current]] passing through a [[circuit]]. If the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] is constant then the [[Electrical Current|current]] decreases as [[temperature]] decreases. | ||
: A '''thermistor''' can be used to control the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] of another [[Electrical Component|component]] in [[Series Circuit|series]] with it. If the [[temperature]] is decreased then the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across other [[Electrical Component|components]] will decrease. | : A '''thermistor''' can be used to control the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] of another [[Electrical Component|component]] in [[Series Circuit|series]] with it. If the [[temperature]] is decreased then the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across other [[Electrical Component|components]] will decrease. | ||
: '''Thermistors''' can be used [[temperature]] sensors. | : '''Thermistors''' can be used [[temperature]] sensors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===IV Graph=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |[[File:IVGraphThermistor.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Description==== | ||
| + | The [[IV Graph]] for an 'NTC' [[thermistor]] shows that: | ||
| + | *At a high [[temperature]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] increases rapidly with the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] | ||
| + | *At a low [[temperature]] the [[Electrical Current|current]] increases slowly with the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Explanation==== | ||
| + | : The [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] of an 'NTC' [[thermistor]] increases as the [[temperature]] decreases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Obtaining the IV Graph==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ThermistorIVGraphCircuit.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" | | ||
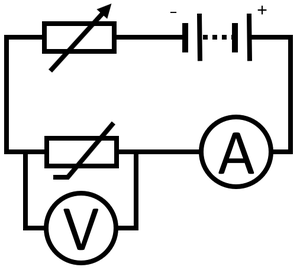
| + | #Connect an [[ammeter]] in [[Series Circuit|series]] with the [[thermistor]] to measure [[Electrical Current|current]] through the [[thermistor]]. | ||
| + | #Connect a [[voltmeter]] in [[Parallel Circuit|parallel]] with the [[thermistor]] to measure the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across it. | ||
| + | #Use a [[Variable Resistor|variable resistor]] in [[Series Circuit|series]] with the [[thermistor]] to vary the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the [[thermistor]]. | ||
| + | #Place the [[thermistor]] in a [[beaker]] of cold [[water]] around 5°C. | ||
| + | #Start with a [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] of zero and increase the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] by an interval of 0.2V up to 2V. | ||
| + | #Recording the reading on the [[voltmeter]] and [[ammeter]]. | ||
| + | #Reverse the connections on the [[battery]] and repeat steps 4 and 5 to find the I-V relationship for negative [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] and [[Electrical Current|current]]. | ||
| + | #Repeat steps 5-7 with the [[thermistor]] in a [[beaker]] of hot [[water]] around 40°C. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Thermistor, pages 47, 52, 64-5, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10356 ''Thermistors, page 184, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac452 ''Thermistors, page 27, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Thermistors, page 57, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Thermistors, pages 293, 298-9, 316-17, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Thermistors, pages 43-4, 64-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Thermistors, pages 60, 80, 81, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Thermistors, pages 62, 82, 83, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Thermistors, page 149, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Thermistors, page 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Thermistors, page 74, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Thermistors, pages 225, 226, 229, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Thermistors, page 179, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945687/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945687&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a598e52189317a20311d7a632747bc9 ''Thermistors, page 47, Gateway GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Thermistors, pages 108-109, 112, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:45, 20 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A thermistor is a resistor which changes resistance depending on the temperature.
About Thermistors
- 'NTC' thermistors decrease resistance as the temperature increases. (NTC = Negative Temperature Coefficient.)
- A thermistor can be used to control the current passing through a circuit. If the potential difference is constant then the current decreases as temperature decreases.
- A thermistor can be used to control the potential difference of another component in series with it. If the temperature is decreased then the potential difference across other components will decrease.
- Thermistors can be used temperature sensors.
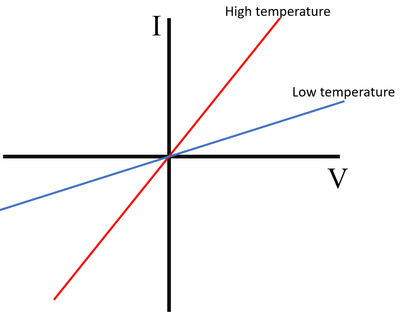
IV Graph
Description
The IV Graph for an 'NTC' thermistor shows that:
- At a high temperature the current increases rapidly with the potential difference
- At a low temperature the current increases slowly with the potential difference.
Explanation
- The resistance of an 'NTC' thermistor increases as the temperature decreases.
Obtaining the IV Graph
|
References
AQA
- Thermistor, pages 47, 52, 64-5, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Thermistors, page 184, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Thermistors, page 27, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Thermistors, page 57, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Thermistors, pages 293, 298-9, 316-17, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Thermistors, pages 43-4, 64-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Thermistors, pages 60, 80, 81, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Thermistors, pages 62, 82, 83, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Thermistors, page 149, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Thermistors, page 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Thermistors, page 74, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Thermistors, pages 225, 226, 229, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel